Advanced Install Options
FREE Veeam Kasten Edition and Licensing
By default, Veeam Kasten comes with an embedded free edition license. The free edition license allows you to use the software on a cluster with at most 50 worker nodes in the first 30 days, and then 5 nodes after the 30-day period. In order to continue using the free license, regular updates to stay within the 6 month support window might be required. You can remove the node restriction of the free license by updating to Enterprise Edition and obtaining the appropriate license from the Kasten team.
Using a Custom License During Install
To install a license that removes the node restriction, please add the
following to any of the helm install commands:
--set license=<license-text>
or, to install a license from a file:
--set-file license=<path-to-license-file>
Veeam Kasten dynamically retrieves the license key and a pod restart is not required.
Changing Licenses
To add a new license to Veeam Kasten, a secret needs to be created in
the Veeam Kasten namespace (default is kasten-io) with the requirement
that the license text be set in a field named license. To do this from
the command line, run:
$ kubectl create secret generic <license-secret-name> \
--namespace kasten-io \
--from-literal=license="<license-text>"
or, to add a license from a file:
$ kubectl create secret generic <license-secret-name> \
--namespace kasten-io \
--from-file=license="<path-to-license-file>"
Multiple license secrets can exist simultaneously and Veeam Kasten will check if any are valid. This license check is done periodically and so, no Veeam Kasten restarts are required if a different existing license becomes required (e.g., due to a cluster expansion or an old license expiry) or when a new license is added.
The resulting license will look like:
apiVersion: v1
data:
license: Y3Vz...
kind: Secret
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2020-04-14T23:50:05Z"
labels:
app: k10
app.kubernetes.io/instance: k10
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
app.kubernetes.io/name: k10
helm.sh/chart: k10-8.5.3
heritage: Helm
release: k10
name: k10-custom-license
namespace: kasten-io
type: Opaque
Similarly, old licenses can be removed by deleting the secret that contains it.
$ kubectl delete secret <license-secret-name> \
--namespace kasten-io
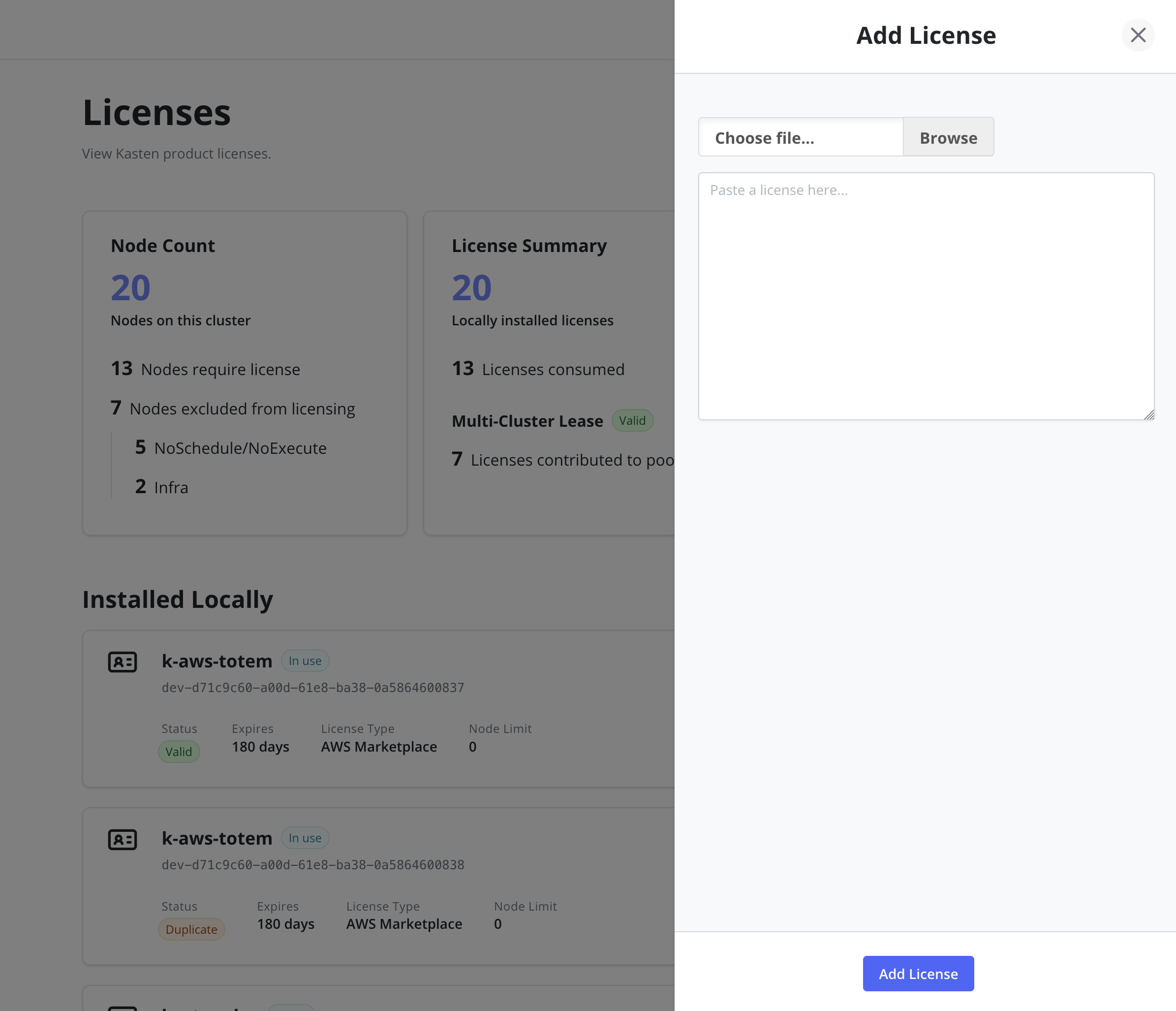
Add Licenses via Dashboard
It is possible to add a license via the Licenses page of the
Settings menu in the navigation sidebar. The license can be pasted
directly into the text field or loaded from a .lic file.
License Grace period
If the license status of the cluster becomes invalid (e.g., the licensed node limit is exceeded), the ability to perform manual actions or creating new policies will be disabled but some previously scheduled policies will continue to run for 30 days. The displayed warning will be look like:
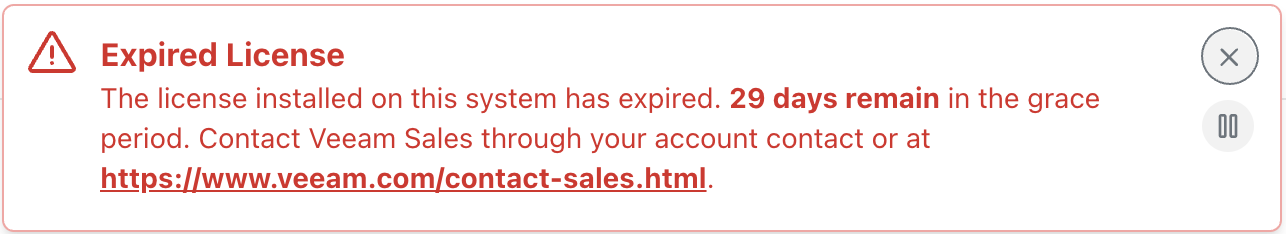
By default, Veeam Kasten provides a grace period of 30 days for Enterprise licenses to ensure that applications remain protected while a new license is obtained or the cluster is brought back into compliance by reducing the number of nodes. Veeam Kasten will stop the creation of any new jobs (scheduled or manual) after the grace period expires.
If the cluster's license status frequently swaps between valid and invalid states, the amount of time the cluster license spends in an invalid status will be subtracted from subsequent grace periods.
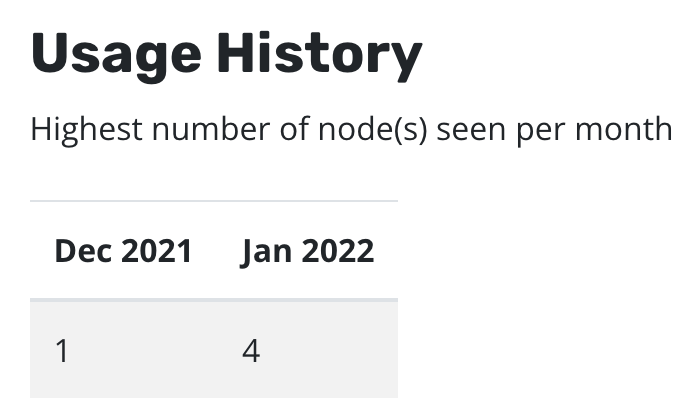
You can see node usage from the last two months via the Licenses page
of the Settings menu in the navigation sidebar. Usage starts being
tracked from the installation date of 4.5.8+. From 5.0.11+ you can see
the same information through
Prometheus.
Manually Creating or Using an Existing Service Account
For more information regarding ServiceAccount restrictions with Kasten,
please refer to this [documentation](../restrictions.md#cluster-admin-restrictions).
The following instructions can be used to create a new Service Account
that grants Veeam Kasten the required permissions to Kubernetes
resources and the use the given Service Account as a part of the install
process. The instructions assume that you will be installing Veeam
Kasten in the kasten-io namespace.
# Create kasten-io namespace if have not done it yet.
$ kubectl create namespace kasten-io
# Create a ServiceAccount for k10 k10-sa
$ kubectl --namespace kasten-io create sa k10-sa
# Create a cluster role binding for k10-sa
$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding k10-sa-rb \
--clusterrole cluster-admin \
--serviceaccount=kasten-io:k10-sa
Following the SA creation, you can install Veeam Kasten using:
$ helm install k10 kasten/k10 --namespace=kasten-io \
--set rbac.create=false \
--set serviceAccount.create=false \
--set serviceAccount.name=k10-sa
Pinning Veeam Kasten to Specific Nodes
While not generally recommended, there might be situations (e.g., test environments, nodes reserved for infrastructure tools, or clusters without autoscaling enabled) where Veeam Kasten might need to be pinned to a subset of nodes in your cluster. You can do this easily with an existing deployment by using a combination of NodeSelectors and Taints and Tolerations.
The process to modify a deployment to accomplish this is demonstrated in
the following example. The example assumes that the nodes you want to
restrict Veeam Kasten to have the label selector-key: selector-value
and a taint set to taint-key=taint-value:NoSchedule.
$ cat << EOF > patch.yaml
spec:
template:
spec:
nodeSelector:
selector-key: selector-value
tolerations:
- key: "taint-key"
operator: "Equal"
value: "taint-value"
effect: "NoSchedule"
EOF
$ kubectl get deployment --namespace kasten-io | awk 'FNR == 1 {next} {print $1}' \
| xargs -I DEP kubectl patch deployments DEP --namespace kasten-io --patch "$(cat patch.yaml)"
Using Trusted Root Certificate Authority Certificates for TLS
For temporary testing of object storage systems that are deployed using self-signed certificates signed by a trusted Root CA, it is also possible to disable certificate verification if the Root CA certificate is not easily available.
If the S3-compatible object store configured in a Location Profile was
deployed with a self-signed certificate that was signed by a trusted
Root Certificate Authority (Root CA), then the certificate for such a
certificate authority has to be provided to Veeam Kasten to enable
successful verification of TLS connections to the object store.
Similarly, to authenticate with a private OIDC provider whose self-signed certificate was signed by a trusted Root CA, the certificate for the Root CA has to be provided to Veeam Kasten to enable successful verification of TLS connections to the OIDC provider.
Multiple Root CAs can be bundled together in the same file.
Install Root CA in Veeam Kasten's namespace
Assuming Veeam Kasten will be deployed in the kasten-io namespace, the
following instructions will make a private Root CA certificate available
to Veeam kasten.
$ kubectl --namespace kasten-io create configmap <configmap-name> --from-file=<custom-bundle-file>.pem
Replace <custom-bundle-file> with the desired filename
To provide the Root CA certificate to Veeam Kasten, add the following to the Helm install command.
--set cacertconfigmap.name=<configmap-name>
--set cacertconfigmap.key=<configmap-key>
Replace <configmap-key> with the desired key
Use of cacertconfigmap.key is optional. If it is unspecified,
the ConfigMap referenced by cacertconfigmap.name must use
the expected default key name, custom-ca-bundle.pem.
Install Root CA in Application's Namespace When Using Kanister Sidecar
If you either use Veeam Kasten's Kanister sidecar injection feature for injecting the Kanister sidecar in your application's namespace or if you have manually added the Kanister sidecar, you must create a ConfigMap containing the Root CA in the application's namespace and update the application's specification so that the ConfigMap is mounted as a Volume. This will enable the Kanister sidecar to verify TLS connections successfully using the Root CA in the ConfigMap.
Assuming that the application's namespace is named test-app, use the
following command to create a ConfigMap containing the Root CA in the
application's namespace:
$ kubectl --namespace test-app create configmap <configmap-name> --from-file= <custom-bundle-file>.pem
Replace <configmap-name> with any desired ConfigMap name and <custom-bundle-file> with the desired filename
This is an example of a VolumeMount that must be added to the application's specification.
- name: custom-ca-bundle-store
mountPath: "/etc/ssl/certs/<custom-bundle-file>.pem"
subPath:<custom-bundle-file>.pem
This is an example of a Volume that must be added to the application's specification.
- name: custom-ca-bundle-store
configMap:
name: custom-ca-bundle-store
Troubleshooting
If Veeam Kasten is deployed without the cacertconfigmap.name setting,
validation failures such as the one shown below will be seen while
configuring a Location Profile using the web based user interface.

In the absence of the cacertconfigmap.name setting, authentication
with a private OIDC provider will fail. Veeam Kasten's logs will show
an error x509: certificate signed by unknown authority.
If you do not install the Root CA in the application namespace when
using a Kanister sidecar with the application, the logs will show an
error x509: certificate signed by unknown authority when the sidecar
tries to connect to any endpoint that requires TLS verification.
Running Veeam Kasten Containers as a Specific User
Veeam Kasten service containers run with UID and fsGroup 1000 by
default. If the storage class Veeam Kasten is configured to use for its
own services requires the containers to run as a specific user, then the
user can be modified.
This is often needed when using shared storage, such as NFS/SMB, where permissions on the target storage require a specific user.
To run as a specific user (e.g., root (0), add the following to the Helm install command:
--set services.securityContext.runAsUser=0 \
--set services.securityContext.fsGroup=0 \
--set prometheus.server.securityContext.runAsUser=0 \
--set prometheus.server.securityContext.runAsGroup=0 \
--set prometheus.server.securityContext.runAsNonRoot=false \
--set prometheus.server.securityContext.fsGroup=0
Other
SecurityContext
settings for the Veeam Kasten service containers can be specified using
the --set service.securityContext.<setting name> and
--set prometheus.server.securityContext.<setting name> options.
Configuring Prometheus
Prometheus is an open-source system monitoring and alerting toolkit bundled with Veeam Kasten.
When passing value from the command line, the value key has to be
prefixed with the prometheus. string:
--set prometheus.server.persistentVolume.storageClass=default.sc
When passing values in a YAML file, all prometheus settings should be
under the prometheus key:
# values.yaml
# global values - apply to both Veeam Kasten and prometheus
global:
persistence:
storageClass: default-sc
# Veeam Kasten specific settings
auth:
basicAuth: enabled
# prometheus specific settings
prometheus:
server:
persistentVolume:
storageClass: another-sc
To modify the bundled Prometheus configuration, only use the helm values listed in the Complete List of Veeam Kasten Helm Options. Any undocumented configurations may affect the functionality of the Veeam Kasten. Additionally, Veeam Kasten does not support disabling Prometheus service, which may lead to unsupported scenarios, potential monitoring and logging issues, and overall functionality disruptions. It is recommended to keep these services enabled to ensure proper functionality and prevent unexpected behavior.
Complete List of Veeam Kasten Helm Options
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
auth.basicAuth.enabled |
Enables basic authentication to the K10 dashboard that allows users to login with username and password | false |
auth.basicAuth.htpasswd |
A username and password pair separated by a colon character | "" |
auth.basicAuth.secretName |
Name of an existing Secret that contains a file generated with htpasswd | "" |
auth.groupAllowList |
A list of groups whose members are allowed access to K10's dashboard | [] |
auth.k10AdminGroups |
A list of groups whose members are granted admin level access to K10's dashboard | [] |
auth.k10AdminUsers |
A list of users who are granted admin level access to K10's dashboard | [] |
auth.ldap.bindDN |
The Distinguished Name(username) used for connecting to the AD/LDAP host | "" |
auth.ldap.bindPWSecretName |
The name of the secret that contains the password corresponding to the bindDN for connecting to the AD/LDAP host |
"" |
auth.ldap.bindPW |
The password corresponding to the bindDN for connecting to the AD/LDAP host |
"" |
auth.ldap.dashboardURL |
The URL used for accessing K10's dashboard | "" |
auth.ldap.enabled |
Enable Active Directory/LDAP based authentication to access K10 dashboard | false |
auth.ldap.groupnameClaim |
Name of a custom OpenID Connect claim for specifying user groups | "groups" |
auth.ldap.groupnamePrefix |
Prefix for user group name | "" |
auth.ldap.groupSearch.baseDN |
The base Distinguished Name to start the AD/LDAP group search from | "" |
auth.ldap.groupSearch.filter |
Optional filter to apply when searching the directory for groups | "" |
auth.ldap.groupSearch.nameAttr |
The AD/LDAP attribute that represents a group's name in the directory | "" |
auth.ldap.groupSearch.userMatchers.groupAttr |
Attribute in the group's entry that must match with the userAttr while searching for groups |
"" |
auth.ldap.groupSearch.userMatchers |
List of field pairs that are used to match a user to a group. | [] |
auth.ldap.groupSearch.userMatchers.userAttr |
Attribute in the user's entry that must match with the groupAttr while searching for groups |
"" |
auth.ldap.host |
Host and optional port of the AD/LDAP server in the form host:port |
"" |
auth.ldap.insecureNoSSL |
Set if the AD/LDAP host is not using TLS | false |
auth.ldap.insecureSkipVerifySSL |
Turn off SSL verification of connections to the AD/LDAP host | false |
auth.ldap.restartPod |
To force a restart of the authentication service Pod (useful when updating authentication config) | false |
auth.ldap.secretName |
The Kubernetes Secret that contains OIDC settings | "" |
auth.ldap.startTLS |
When set to true, ldap:// is used to connect to the server followed by creation of a TLS session. When set to false, ldaps:// is used. | false |
auth.ldap.usernameClaim |
The claim to be used as the username | "email" |
auth.ldap.usernamePrefix |
Prefix that has to be used with the username obtained from the username claim | "" |
auth.ldap.userSearch.baseDN |
The base Distinguished Name to start the AD/LDAP search from | "" |
auth.ldap.userSearch.emailAttr |
AD/LDAP attribute in a user's entry that should map to the email field in a token | "" |
auth.ldap.userSearch.filter |
Optional filter to apply when searching the directory | "" |
auth.ldap.userSearch.idAttr |
AD/LDAP attribute in a user's entry that should map to the user ID field in a token | "" |
auth.ldap.userSearch.nameAttr |
Attribute in a user's entry that should map to the name field in a token | "" |
auth.ldap.userSearch.preferredUsernameAttr |
AD/LDAP attribute in a user's entry that should map to the preferred_username field in a token | "" |
auth.ldap.userSearch.username |
Attribute used for comparing user entries when searching the directory | "" |
auth.oidcAuth.clientID |
Client ID given by the OIDC provider for K10 | "" |
auth.oidcAuth.clientSecret |
Client secret given by the OIDC provider for K10 | "" |
auth.oidcAuth.clientSecretName |
The secret that contains the Client ID and Client secret given by the OIDC provider for K10 | "" |
auth.oidcAuth.enabled |
Enable Open ID Connect based authentication to access K10 dashboard | false |
auth.oidcAuth.groupClaim |
Name of a custom OpenID Connect claim for specifying user groups | "" |
auth.oidcAuth.groupPrefix |
All groups will be prefixed with this value to prevent conflicts | "" |
auth.oidcAuth.logoutURL |
URL to your OIDC provider's logout endpoint | "" |
auth.oidcAuth.prompt |
The type of prompt to be used during authentication (none, consent, login or select_account) | "select_account" |
auth.oidcAuth.providerURL |
URL for the OIDC Provider | "" |
auth.oidcAuth.redirectURL |
URL to the K10 gateway service | "" |
auth.oidcAuth.refreshTokenSupport |
Enable OIDC Refresh Token support. Disabled by default. | false |
auth.oidcAuth.scopes |
Space separated OIDC scopes required for userinfo. Example: "profile email" | "" |
auth.oidcAuth.secretName |
Must include providerURL, redirectURL, scopes, clientID/secret and logoutURL | "" |
auth.oidcAuth.sessionDuration |
Maximum OIDC session duration. Default value is 1 hour | "1h" |
auth.oidcAuth.usernameClaim |
The claim to be used as the username | "" |
auth.oidcAuth.usernamePrefix |
Prefix that has to be used with the username obtained from the username claim | "" |
auth.openshift.caCertsAutoExtraction |
Set this to false to disable the OCP CA certificates automatic extraction to the K10 namespace | true |
auth.openshift.clientSecretName |
The secret that contains the token corresponding to the service account | "" |
auth.openshift.clientSecret |
The token corresponding to the service account | "" |
auth.openshift.dashboardURL |
The URL used for accessing K10's dashboard | "" |
auth.openshift.enabled |
Enables access to the K10 dashboard by authenticating with the OpenShift OAuth server | false |
auth.openshift.groupnameClaim |
Name of a custom OpenID Connect claim for specifying user groups | "groups" |
auth.openshift.groupnamePrefix |
Prefix for user group name | "" |
auth.openshift.insecureCA |
To turn off SSL verification of connections to OpenShift | false |
auth.openshift.openshiftURL |
The URL for accessing OpenShift's API server | "" |
auth.openshift.secretName |
Specify Kubernetes Secret that contains OIDC settings | "" |
auth.openshift.serviceAccount |
Name of the service account that represents an OAuth client | "" |
auth.openshift.usernameClaim |
The claim to be used as the username | "email" |
auth.openshift.usernamePrefix |
Prefix that has to be used with the username obtained from the username claim | "" |
auth.openshift.useServiceAccountCA |
Usually found at /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt |
false |
auth.tokenAuth.enabled |
Enable token based authentication to access K10 dashboard | false |
awsConfig.assumeRoleDuration |
The minimum value is 15 minutes, and the maximum value is determined by the maximum session duration setting for that IAM role. For documentation on how to view and edit the maximum session duration for an IAM role, refer to https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_roles_use.html#id_roles_use_view-role-max-session. The value accepts a number followed by a single character, 'm' (for minutes) or 'h' (for hours). Examples include: 60m or 2h | "" |
awsConfig.efsBackupVaultName |
Specifies the AWS EFS backup vault name | "k10vault" |
azure.useDefaultMSI |
Set to true - profile does not need a secret, Default Managed Identity will be used | false |
azure.useFederatedIdentity |
Set to true - injected Federated Identity will be used | false |
cacertconfigmap.key |
Key of the K8s ConfigMap containing a certificate for a trusted root certificate authority | "" |
cacertconfigmap.name |
Name of the K8s ConfigMap containing a certificate for a trusted root certificate authority | "" |
cluster.domainName |
Specifies the domain name of the cluster | "" |
clusterName |
Cluster name for better logs visibility | "" |
datastore.parallelBlockDownloads |
Specifies how many blocks can be downloaded in parallel from the data store | 8 |
datastore.parallelBlockUploads |
Specifies how many blocks can be uploaded in parallel to the data store | 8 |
datastore.parallelDownloads |
Specifies how many files can be downloaded in parallel from the data store | 8 |
datastore.parallelUploads |
Specifies how many files can be uploaded in parallel to the data store | 8 |
defaultPriorityClassName |
Specifies the default priority class name for all K10 deployments and ephemeral Pods | "" |
encryption.primaryKey.awsCmkKeyId |
Specifies the AWS CMK key ID for encrypting K10 Primary Key | "" |
encryption.primaryKey.azureKeyVaultKeyName |
Specifies the Azure Key Vault key name for encrypting K10 Primary Key | "" |
encryption.primaryKey.azureKeyVaultURL |
Specifies the Azure Key Vault URL which holds the key for encrypting K10 Primary Key | "" |
encryption.primaryKey.vaultTransitKeyName |
Vault Transit key name for Vault integration | "" |
encryption.primaryKey.vaultTransitPath |
Vault transit path for Vault integration | "" |
ephemeralPVCOverhead |
Set the percentage increase for the ephemeral Persistent Volume Claim's storage request, e.g. pvc size = (file raw size) * (1 + ephemeralPVCOverhead) |
"0.1" |
eula.accept |
Whether to enable accept EULA before installation | false |
excludedApps |
Specifies a list of applications to be excluded from the dashboard & compliance considerations. Format should be a YAML array | ["kube-system","kube-ingress","kube-node-lease","kube-public","kube-rook-ceph"] |
externalGateway.annotations |
Standard annotations for the services | {} |
externalGateway.awsSSLCertARN |
ARN for the AWS ACM SSL certificate used in the K10 API server | "" |
externalGateway.create |
Create external gateway service | false |
externalGateway.fqdn.name |
Domain name for the K10 API services | "" |
externalGateway.fqdn.type |
Supported gateway type: route53-mapper or external-dns | "" |
fips.enabled |
Specifies whether K10 should be run in the FIPS mode of operation | false |
forceRootInBlueprintActions |
Forces any Pod created by a Blueprint to run as root user | true |
frs.maxMountsPerNamespace |
Sets the maximum number of volume mounts permitted concurrently across all active FileRecoverySession objects in a single Namespace | 4 |
frs.maxMountsPerSession |
Sets the maximum number of volume mounts permitted in a single FileRecoverySession object | 4 |
frs.maxSystemMounts |
Sets the maximum number of volume mounts permitted concurrently across all active FileRecoverySession objects in the cluster | 16 |
frs.sessionExpiryTimeInMinutes |
Specifies, in minutes, the maximum duration of a FileRecoverySession object | 30 |
garbagecollector.actions.enabled |
Set true to enable action collectors | false |
garbagecollector.daemonPeriod |
Sets garbage collection period (in seconds) | 21600 |
garbagecollector.keepMaxActions |
Sets maximum actions to keep | 1000 |
gateway.resources.limits.cpu |
Gateway Pod cpu limit | "1000m" |
gateway.resources.limits.ephemeral-storage |
Gateway Pod ephemeral storage limit | "" |
gateway.resources.limits.memory |
Gateway Pod memory limit | "1Gi" |
gateway.resources.requests.cpu |
Gateway Pod cpu request | "200m" |
gateway.resources.requests.ephemeral-storage |
Gateway Pod ephemeral storage request | "" |
gateway.resources.requests.memory |
Gateway Pod memory request | "300Mi" |
gateway.service.externalPort |
Specifies the gateway services external port | 80 |
genericStorageBackup.token |
Token to enable generic volume snapshot | "" |
genericVolumeSnapshot.resources.limits.cpu |
Generic Volume Snapshot restore Pods cpu limit | "" |
genericVolumeSnapshot.resources.limits.ephemeral-storage |
Generic Volume Snapshot restore Pods ephemeral storage limit | "" |
genericVolumeSnapshot.resources.limits.memory |
Generic Volume Snapshot restore Pods memory limit | "" |
genericVolumeSnapshot.resources.requests.cpu |
Generic Volume Snapshot restore Pods cpu request | "" |
genericVolumeSnapshot.resources.requests.ephemeral-storage |
Generic Volume Snapshot restore Pods ephemeral storage request | "" |
genericVolumeSnapshot.resources.requests.memory |
Generic Volume Snapshot restore Pods memory request | "" |
global.acm.enabled |
Enable ACM integration | false |
global.acm.hubThanosTenantId |
Hub Thanos Tenant ID for ACM | "" |
global.acm.managedClusterId |
Managed Cluster ID for ACM | "" |
global.airgapped.repository |
Specify the helm repository for offline (airgapped) installation | "" |
global.ephemeralResourceLabels |
Configures custom labels to be set on all Kasten ephemeral PVCs, Network Policies, Services, and Pods. Takes precedence over keys also set in global.resourceLabels on ephemeral resources. | {} |
global.imagePullSecret |
Provide secret which contains docker config for private repository. Use k10-ecr when secrets.dockerConfigPath is used. |
"" |
global.network.enable_ipv6 |
Enable IPv6 support for K10 |
false |
global.persistence.catalog.size |
If not set, global.persistence.size is used. | "" |
global.persistence.jobs.size |
If not set, global.persistence.size is used. | "" |
global.persistence.logging.size |
If not set, global.persistence.size is used. | "" |
global.persistence.metering.size |
If not set, global.persistence.size is used | "2Gi" |
global.persistence.size |
Change default size for Persistent Volumes | "20Gi" |
global.persistence.storageClass |
If set to '-', dynamic provisioning is disabled. If undefined (the default) or set to null, the default provisioner is used. (e.g gp2 on AWS, standard on GKE, AWS & OpenStack) | "" |
global.podAnnotations |
Configures custom annotations to be set to all Kasten Pods | {} |
global.podLabels |
DEPRECATED: Configures custom labels to be set to all Kasten Pods | {} |
global.prometheus.external.baseURL |
Provide Base URL of external prometheus | "" |
global.prometheus.external.host |
Provide external prometheus host name | "" |
global.prometheus.external.port |
Provide external prometheus port number | "" |
global.resourceLabels |
Configures custom labels to be set on all Kasten PVCs, Network Policies, Services, and Pods. | {} |
global.resources.limits |
Global resource limits to be added to each Kasten service unless overridden by service specific values | {} |
global.resources.requests |
Global resource requests to be added to each Kasten service unless overridden by service specific values | {} |
google.workloadIdentityFederation.enabled |
Enable Google Workload Identity Federation for K10 | false |
google.workloadIdentityFederation.idp.aud |
Audience for whom the ID Token from Identity Provider is intended | "" |
google.workloadIdentityFederation.idp.type |
Identity Provider type for Google Workload Identity Federation for K10 | "" |
grafana.external.url |
If Grafana instance that gets installed with K10 is disabled using grafana.enabled=false, this field can be used to specify URL of externally installed Grafana instance. | "" |
ingress.annotations |
Add optional annotations to the Ingress resource | {} |
ingress.class |
Cluster ingress controller class: nginx, GCE |
"" |
ingress.create |
Specifies whether the K10 dashboard should be exposed via ingress | false |
ingress.defaultBackend.resource.apiGroup |
Optional API group of a resource backing the default backend. | "" |
ingress.defaultBackend.resource.enabled |
Configures the default backend backed by a resource for the K10 dashboard Ingress (mutually exclusive setting with ingress.defaultBackend.service.enabled). |
false |
ingress.defaultBackend.resource.kind |
The type of a resource being referenced by the default backend (required if the resource default backend is used). | "" |
ingress.defaultBackend.resource.name |
Name of a resource referenced by the default backend. | "" |
ingress.defaultBackend.service.enabled |
Configures the default backend backed by a service for the K10 dashboard Ingress (mutually exclusive setting with ingress.defaultBackend.resource.enabled). |
false |
ingress.defaultBackend.service.name |
Name of a service referenced by the default backend. | "" |
ingress.defaultBackend.service.port.name |
Port name of a service referenced by the default backend (mutually exclusive with number). |
"" |
ingress.defaultBackend.service.port.number |
Port number of a service referenced by the default backend (mutually exclusive with name). |
0 |
ingress.host |
FQDN (e.g., k10.example.com) for name-based virtual host |
"" |
ingress.name |
Optional name of the Ingress object for the K10 dashboard. Defaults to {Release.Name}-ingress | "" |
ingress.pathType |
Set the path type for the ingress resource | "ImplementationSpecific" |
ingress.tls.enabled |
Configures a TLS use for ingress.host |
false |
ingress.tls.secretName |
Optional TLS secret name | "" |
ingress.urlPath |
URL path for K10 Dashboard. Defaults to {Release.Name} | "" |
injectGenericVolumeBackupSidecar.enabled |
Enables injection of sidecar container required to perform Generic Volume Backup into workload Pods | false |
injectGenericVolumeBackupSidecar.namespaceSelector.matchLabels |
Set of labels to select namespaces in which sidecar injection is enabled for workloads | {} |
injectGenericVolumeBackupSidecar.objectSelector.matchLabels |
Set of labels to filter workload objects in which the sidecar is injected | {} |
injectGenericVolumeBackupSidecar.webhookServer.port |
Port number on which the mutating webhook server accepts request | 8080 |
kanister.managedDataServicesBlueprintsEnabled |
Whether to enable built-in Kanister Blueprints for data services such as Crunchy Data Postgres Operator and K8ssandra | true |
kastenDisasterRecovery.quickMode.enabled |
Enables Veeam Kasten Disaster Recovery Quick mode | true |
kastenDisasterRecovery.restoreTimeout |
Sets the maximum duration (in minutes) for a restore operation to complete | 90 |
kastenDisasterRecovery.validationTimeout |
Sets the maximum duration (in minutes) for a validation operation to complete | 30 |
kubeVirtVMs.snapshot.unfreezeTimeout |
Specifies the duration within which a VM must be unfrozen before aborting a freeze operation and proceeding with a crash consistent snapshot. The minimum value is 10s |
"5m" |
license |
Add license string obtained from Kasten | "" |
limiter.csiSnapshotRestoresPerAction |
Per action limit of concurrent CSI volume provisioning requests when restoring from VolumeSnapshots | 3 |
limiter.csiSnapshotsPerCluster |
Cluster-wide limit of concurrent CSI VolumeSnapshot creation requests | 10 |
limiter.directSnapshotsPerCluster |
Cluster-wide limit of concurrent non-CSI snapshot creation requests | 10 |
limiter.executorReplicas |
Specifies the number of executor-svc Pods used to process Kasten jobs | 3 |
limiter.executorThreads |
Specifies the number of threads per executor-svc Pod used to process Kasten jobs | 8 |
limiter.genericVolumeBackupsPerCluster |
Cluster-wide limit of concurrent Generic Volume Backup operations | 10 |
limiter.imageCopiesPerCluster |
Cluster-wide limit of concurrent ImageStream container image backup (i.e. copy from) and restore (i.e. copy to) operations | 10 |
limiter.snapshotExportsPerAction |
Per action limit of concurrent volume export operations | 3 |
limiter.snapshotExportsPerCluster |
Cluster-wide limit of concurrent volume export operations | 10 |
limiter.vmSnapshotsPerCluster |
Cluster-wide limit of concurrent virtual machine snapshot operations | 1 |
limiter.volumeRestoresPerAction |
Per action limit of concurrent volume restore operations from an exported backup | 3 |
limiter.volumeRestoresPerCluster |
Cluster-wide limit of concurrent volume restore operations from exported backups | 10 |
limiter.workloadRestoresPerAction |
Per action limit of concurrent manifest data restores, based on workload (ex. Namespace, Deployment, StatefulSet, VirtualMachine) | 3 |
limiter.workloadSnapshotsPerAction |
Per action limit of concurrent manifest data snapshots, based on workload (ex. Namespace, Deployment, StatefulSet, VirtualMachine) | 5 |
logLevel |
Change default log level | "info" |
metering.awsManagedLicense |
Set AWS managed license mode | false |
metering.awsMarketplace |
Set AWS cloud metering license mode | false |
metering.awsRegion |
Set AWS_REGION for metering service | "" |
metering.licenseConfigSecretName |
AWS managed license config secret | "" |
metering.mode |
Control license reporting (set to airgap for private-network installs) |
"" |
metering.promoID |
K10 promotion ID from marketing campaigns | "" |
metering.redhatMarketplacePayg |
Set Red Hat cloud metering license mode | false |
metering.reportCollectionPeriod |
Metric report collection period (in seconds) | 1800 |
metering.reportPushPeriod |
Metric report push period (in seconds) | 3600 |
multicluster.enabled |
Choose whether to enable the multi-cluster system components and capabilities | true |
multicluster.primary.create |
Choose whether to setup cluster as a multi-cluster primary | false |
multicluster.primary.ingressURL |
Choose the dashboard URL for the multi-cluster primary; e.g. https://cluster-name.domain/k10 | "" |
multicluster.primary.name |
Choose the cluster name for multi-cluster primary | "" |
networkPolicy.create |
Whether to create NetworkPolicies for the K10 services | true |
priorityClassName |
Overrides the default priority class name for the specified deployment | {} |
prometheus.alertmanager.enabled |
DEPRECATED: (optional) Enable Prometheus alertmanager service |
false |
prometheus.alertmanager.serviceAccount.create |
DEPRECATED: (optional) Set true to create ServiceAccount for alertmanager |
false |
prometheus.k10image.registry |
(optional) Set Prometheus image registry. | gcr.io |
prometheus.k10image.repository |
(optional) Set Prometheus image repository. | kasten-images |
prometheus.networkPolicy.enabled |
DEPRECATED: (optional) Enable Prometheus networkPolicy |
false |
prometheus.prometheus-node-exporter.enabled |
DEPRECATED: (optional) Enable Prometheus node-exporter |
false |
prometheus.prometheus-node-exporter.serviceAccount.create |
DEPRECATED: (optional) Set true to create ServiceAccount for prometheus-node-exporter |
false |
prometheus.prometheus-pushgateway.enabled |
DEPRECATED: (optional) Enable Prometheus pushgateway |
false |
prometheus.prometheus-pushgateway.serviceAccount.create |
DEPRECATED: (optional) Set true to create ServiceAccount for prometheus-pushgateway |
false |
prometheus.rbac.create |
(optional) Whether to create Prometheus RBAC configuration. Warning - this action will allow prometheus to scrape Pods in all k8s namespaces | false |
prometheus.scrapeCAdvisor |
DEPRECATED: (optional) Enable Prometheus ScrapeCAdvisor | false |
prometheus.server.baseURL |
(optional) K10 Prometheus external url path at which the server can be accessed | "/k10/prometheus/" |
prometheus.server.configMapOverrideName |
DEPRECATED: (optional) Prometheus configmap name to override default generated name | k10-prometheus-config |
prometheus.server.enabled |
(optional) If false, K10's Prometheus server will not be created, reducing the dashboard's functionality. | true |
prometheus.server.fullnameOverride |
(optional) Prometheus deployment name to override default generated name | "prometheus-server" |
prometheus.server.persistentVolume.enabled |
DEPRECATED: (optional) If true, K10 Prometheus server will create a Persistent Volume Claim | true |
prometheus.server.persistentVolume.size |
(optional) K10 Prometheus server data Persistent Volume size | "8Gi" |
prometheus.server.persistentVolume.storageClass |
(optional) StorageClassName used to create Prometheus PVC. Setting this option overwrites global StorageClass value | "" |
prometheus.server.prefixURL |
(optional) K10 Prometheus prefix slug at which the server can be accessed | "/k10/prometheus" |
prometheus.server.retention |
(optional) K10 Prometheus data retention | "30d" |
prometheus.server.securityContext.fsGroup |
(optional) Set security context fsGroup ID for Prometheus server Pod |
65534 |
prometheus.server.securityContext.runAsGroup |
(optional) Set security context runAsGroup ID for Prometheus server Pod |
65534 |
prometheus.server.securityContext.runAsNonRoot |
(optional) Enable security context runAsNonRoot for Prometheus server Pod |
true |
prometheus.server.securityContext.runAsUser |
(optional) Set security context runAsUser ID for Prometheus server Pod |
65534 |
prometheus.server.serviceAccounts.server.create |
DEPRECATED: (optional) Set true to create ServiceAccount for Prometheus server service | true |
prometheus.server.strategy.rollingUpdate.maxSurge |
DEPRECATED: (optional) The number of Prometheus server Pods that can be created above the desired amount of Pods during an update | "100%" |
prometheus.server.strategy.rollingUpdate.maxUnavailable |
DEPRECATED: (optional) The number of Prometheus server Pods that can be unavailable during the upgrade process | "100%" |
prometheus.server.strategy.type |
DEPRECATED: (optional) Change default deployment strategy for Prometheus server | "RollingUpdate" |
rbac.create |
Toggle RBAC resource creation | true |
resources.<deploymentName>.<containerName>.limits.cpu |
Overwrite the default K10 container cpu limits | "" |
resources.<deploymentName>.<containerName>.limits.memory |
Overwrite the default K10 container memory limits | "" |
resources.<deploymentName>.<containerName>.requests.cpu |
Overwrite the default K10 container cpu request | "" |
resources.<deploymentName>.<containerName>.requests.memory |
Overwrite the default K10 container memory request | "" |
route.annotations |
Additional Route object annotations | {} |
route.enabled |
Specifies whether the K10 dashboard should be exposed via route | false |
route.host |
FQDN (e.g., .k10.example.com) for name-based virtual host |
"" |
route.labels |
Additional Route object labels | {} |
route.path |
Set Path for the route. Defaults to '/' | "" |
route.tls.enabled |
Configures a TLS use for route.host |
false |
route.tls.insecureEdgeTerminationPolicy |
Specifies behavior for insecure scheme traffic | "Redirect" |
route.tls.termination |
Set termination Schema | "edge" |
scc.allowCSI |
Enable/disable the CSI ephemeral volumes in k10 | false |
scc.create |
Toggle creation of SecurityContextConstraints for Kasten ServiceAccount(s) | false |
scc.priority |
Sets the SecurityContextConstraints priority | 0 |
secrets.awsAccessKeyId |
AWS access key ID (required for AWS deployment) | "" |
secrets.awsClientSecretName |
Specify a Secret directly instead of having to provide awsAccessKeyId, awsSecretAccessKey and awsIamRole | "" |
secrets.awsIamRole |
ARN of the AWS IAM role assumed by K10 to perform any AWS operation | "" |
secrets.awsSecretAccessKey |
AWS access key secret | "" |
secrets.azureADEndpoint |
Azure Active Directory login endpoint | "" |
secrets.azureADResourceID |
Azure Active Directory resource ID to obtain AD tokens | "" |
secrets.azureClientId |
Azure Service App ID | "" |
secrets.azureClientSecret |
Azure Service APP secret | "" |
secrets.azureClientSecretName |
Specify a Secret directly instead of having to provide azureClientId, azureTenantId and azureClientSecret | "" |
secrets.azureCloudEnvID |
Azure Cloud Environment ID | "" |
secrets.azureResourceGroup |
Resource Group name that was created for the Kubernetes cluster | "" |
secrets.azureResourceMgrEndpoint |
Resource management endpoint for the Azure Stack instance | "" |
secrets.azureSubscriptionID |
Subscription ID in your Azure tenant | "" |
secrets.azureTenantId |
Azure tenant ID (required for Azure deployment) | "" |
secrets.dockerConfig |
base64 representation of your Docker credentials to pull docker images from a private registry. Alternative to the secrets.dockerConfigPath |
"" |
secrets.dockerConfigPath |
Path to Docker config file to create secret from. Will be overwritten if secrets.dockerConfig is set. |
"" |
secrets.googleApiKey |
Non-default base64 encoded GCP Service Account key | "" |
secrets.googleClientSecretName |
Specify a Secret directly instead of having to provide googleApiKey and googleProjectId | "" |
secrets.googleProjectId |
Set Google Project ID other than the one in the GCP Service Account | "" |
secrets.microsoftEntraIDEndpoint |
Microsoft Entra ID login endpoint | "" |
secrets.microsoftEntraIDResourceID |
Microsoft Entra ID resource ID to obtain AD tokens | "" |
secrets.vsphereClientSecretName |
Specify a Secret directly instead of having to provide vsphereUsername, vspherePassword and vspherePassword | "" |
secrets.vsphereEndpoint |
vSphere endpoint for login | "" |
secrets.vspherePassword |
vSphere password for login | "" |
secrets.vsphereUsername |
vSphere username for login | "" |
serviceAccount.create |
Specifies whether a ServiceAccount should be created | true |
serviceAccount.name |
The name of the ServiceAccount to use. If not set and create is true, a name is derived using the release and chart names | "" |
services.aggregatedapis.hostNetwork |
Whether the aggregatedapis Pods may use the node network | false |
services.dashboardbff.hostNetwork |
Whether the dashboardbff Pods may use the node network | false |
services.executor.hostNetwork |
Whether the executor Pods may use the node network | false |
services.securityContext.fsGroup |
FSGroup that owns K10 service container volumes | 1000 |
services.securityContext.runAsNonRoot |
Indicates that K10 service containers should run as non-root user. | true |
services.securityContext.runAsUser |
User ID K10 service containers run as | 1000 |
services.securityContext.seccompProfile.type |
Sets the Seccomp profile type for K10 service containers | "RuntimeDefault" |
siem.logging.cloud.awsS3.enabled |
Whether to enable sending K10 audit event logs to AWS S3 | true |
siem.logging.cloud.path |
Directory path in cloud object storage for saving logs when writing K10 events | "k10audit/" |
siem.logging.cluster.enabled |
Whether to enable writing K10 audit event logs to stdout (standard output) | true |
timeout.blueprintBackup |
Specifies the timeout (in minutes) for Blueprint backup actions | 45 |
timeout.blueprintDelete |
Specifies the timeout (in minutes) for Blueprint delete actions | 45 |
timeout.blueprintHooks |
Specifies the timeout (in minutes) for Blueprint backupPrehook and backupPosthook actions | 20 |
timeout.blueprintRestore |
Specifies the timeout (in minutes) for Blueprint restore actions | 600 |
timeout.checkRepoPodReady |
Specifies the timeout (in minutes) for temporary worker Pods used to validate backup repository existence | 20 |
timeout.efsRestorePodReady |
Specifies the timeout (in minutes) for temporary worker Pods used for shareable volume restore operations | 45 |
timeout.jobWait |
Specifies the timeout (in minutes) for completing execution of any child job, after which the parent job will be canceled. If no value is set, a default of 10 hours will be used | "" |
timeout.statsPodReady |
Specifies the timeout (in minutes) for temporary worker Pods used to collect repository statistics | 20 |
timeout.workerPodReady |
Specifies the timeout (in minutes) for all other temporary worker Pods used during Veeam Kasten operations | 15 |
vap.kastenPolicyPermissions.enabled |
Set true to enable installation of the VAP for Kasten policies | false |
vault.address |
Specify Vault endpoint | "http://vault.vault.svc:8200" |
vault.mountPath |
Hashicorp Vault auth mount path used with the Kubernetes auth method. Will default to 'kubernetes' if unspecified. | "" |
vault.role |
Role that was bound to the service account name and namespace from cluster | "" |
vault.secretName |
Vault secret name | "" |
vault.serviceAccountTokenPath |
Default: '/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token' | "" |
vmWare.taskTimeoutMin |
the timeout for VMWare operations in minutes | 60 |
workerPodCRDs.defaultActionPodSpec |
The name of ActionPodSpec that will be used by default for worker Pod resources. if empty, the default APS is omitted | "" |
workerPodCRDs.enabled |
Specifies whether K10 should use ActionPodSpec for granular resource control of worker Pods |
false |
workerPodCRDs.resourcesRequests.maxCPU |
Specifies the cluster-wide, maximum value for CPU resource requests which may be used in any ActionPodSpec | "" |
workerPodCRDs.resourcesRequests.maxEphemeralStorage |
Specifies the cluster-wide maximum value for storage volumes that may be attached to any ActionPodSpec | "" |
workerPodCRDs.resourcesRequests.maxMemory |
Specifies the cluster-wide, maximum value for memory resource requests which may be used in any ActionPodSpec | "" |
workerPodMetricSidecar.enabled |
Enables a sidecar container for temporary worker Pods used to push Pod performance metrics to Prometheus | true |
workerPodMetricSidecar.metricLifetime |
Specifies the period after which metrics for an individual worker Pod are removed from Prometheus | "2m" |
workerPodMetricSidecar.pushGatewayInterval |
Specifies the frequency for pushing metrics into Prometheus | "30s" |
workerPodMetricSidecar.resources.limits.cpu |
Temporary worker Pod metric sidecars cpu limit | "" |
workerPodMetricSidecar.resources.limits.ephemeral-storage |
Temporary worker Pod metric sidecars storage limit | "" |
workerPodMetricSidecar.resources.limits.memory |
Temporary worker Pod metric sidecars memory limit | "" |
workerPodMetricSidecar.resources.requests.cpu |
Temporary worker Pod metric sidecars cpu request | "" |
workerPodMetricSidecar.resources.requests.ephemeral-storage |
Temporary worker Pod metric sidecars storage request | "" |
workerPodMetricSidecar.resources.requests.memory |
Temporary worker Pod metric sidecar memory request | "" |
Helm Configuration for Parallel Upload to the Storage Repository
Veeam Kasten provides an option to manage parallelism for
file mode
uploads to the storage repository through a configurable parameter,
datastore.parallelUploads via Helm. To upload N files in parallel to the
storage repository, configure this flag to N. This flag is adjusted
when dealing with larger PVCs to improve performance. By default, the
value is set to 8.
A similar option called datastore.parallelBlockUploads is used to control
how many blocks can be uploaded concurrently when exporting a snapshot in
block mode.
Adjusting this value may be necessary to decrease the upload time for larger
PVCs but comes at a cost of additional memory utilization in the ephemeral
Pod launched for the operation.
By default, the value is set to 8.
These parameters should not be modified unless instructed by the support team.
Helm Configuration for Parallel Download from the Storage Repository
Veeam Kasten provides an option to manage parallelism for
file mode
downloads from the storage repository through a configurable parameter,
datastore.parallelDownloads via Helm. To download N files in parallel from
the storage repository, configure this flag to N. This flag is
adjusted when dealing with larger PVCs to improve performance. By
default, the value is set to 8.
A similar option called datastore.parallelBlockDownloads is used to
control how many blocks can be downloaded concurrently when restoring from a
snapshot exported in block mode.
Adjusting this value may be necessary to decrease the restore time for larger
PVCs but comes at a cost of additional memory utilization in the ephemeral
Pod launched for the operation.
By default, the value is set to 8.
These parameters should not be modified unless instructed by the support team.
Setting Custom Labels and Annotations on Veeam Kasten Resources
Veeam Kasten allows you to apply custom labels and annotations to its resources using the global section of your Helm values.
- Use the
global.resourceLabelsHelm flag to apply labels to all Kasten PersistentVolumeClaims (PVCs), NetworkPolicies, Services, and Pods. - Use the
global.ephemeralResourceLabelsHelm flag to apply labels specifically to Kasten temporary (ephemeral) PVCs, NetworkPolicies, Services, and Pods. If the same key is set in bothglobal.resourceLabelsandglobal.ephemeralResourceLabels, the value fromglobal.ephemeralResourceLabelswill take precedence for ephemeral resources. - Use the
global.podAnnotationsHelm flag to apply annotations to all Kasten pods.
Example values.yaml:
global:
resourceLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: "kasten"
lifecycle: "persistent"
ephemeralResourceLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: "kasten-job"
lifecycle: "ephemeral"
podAnnotations:
config.kubernetes.io/local-config: "true"
kubernetes.io/description: "Description"
Alternatively, you can configure these parameters using the Helm --set flag:
--set global.resourceLabels.labelKey1=value1 --set global.resourceLabels.labelKey2=value2 \
--set global.ephemeralResourceLabels.ephemeralLabelKey1=ephemeralValue1 --set global.ephemeralResourceLabels.ephemeralLabelKey2=ephemeralValue2 \
--set global.podAnnotations.annotationKey1="Example annotation" --set global.podAnnotations.annotationKey2=value2
Labels and annotations passed using these Helm parameters
(global.resourceLabels and global.podAnnotations) apply to the Prometheus pods as well, if it is managed by Veeam
Kasten. However, if labels and annotations are set in the Prometheus sub-chart, they will be prioritized over the global resource labels
and annotations set.