As of March 5, 2024, "Azure Active Directory" has been renamed as "Microsoft Entra ID." Throughout this documentation, references to "Azure Active Directory" will be updated to use both the new and old names. Both names will be used for a while, after which the documentation will be updated to use only the new name.
Storage Integration
Veeam Kasten supports direct integration with public cloud storage vendors as well as CSI integration. While most integrations are transparent, the below sections document the configuration needed for the exceptions.
Direct Provider Integration
Veeam Kasten supports seamless and direct storage integration with a number of storage providers. The following storage providers are either automatically discovered and configured within Veeam Kasten or can be configured for direct integration:
- Amazon Elastic Block Store (EFS)
- Azure Managed Disks (Azure Managed Disks)
- Google Persistent Disk
- Ceph
- Cinder-based providers on OpenStack
- vSphere Cloud Native Storage (CNS)
- Portworx
- Veeam Backup (snapshot data export only)
Container Storage Interface (CSI)
Apart from direct storage provider integration, Veeam Kasten also supports invoking volume snapshots operations via the Container Storage Interface (CSI). To ensure that this works correctly, please ensure the following requirements are met.
CSI Requirements
- Kubernetes v1.14.0 or higher
- The
VolumeSnapshotDataSourcefeature has been enabled in the Kubernetes cluster - A CSI driver that has Volume Snapshot support. Please look at the list of CSI drivers to confirm snapshot support.
Pre-Flight Checks
Assuming that the default kubectl context is pointed to a cluster with CSI enabled, CSI pre-flight checks can be run by deploying the primer tool with a specified StorageClass. This tool runs in a pod in the cluster and performs the following operations:
- Creates a sample application with a persistent volume and writes some data to it
- Takes a snapshot of the persistent volume
- Creates a new volume from the persistent volume snapshot
- Validates the data in the new persistent volume
First, run the following command to derive the list of provisioners along with their StorageClasses and VolumeSnapshotClasses.
curl -s https://docs.kasten.io/downloads/7.5.10/tools/k10_primer.sh | bash
Then, run the following command with a valid StorageClass to deploy the pre-check tool:
curl -s https://docs.kasten.io/downloads/7.5.10/tools/k10_primer.sh | bash /dev/stdin csi -s ${STORAGE_CLASS}
CSI Snapshot Configuration
For each CSI driver, ensure that a VolumeSnapshotClass has been added with Veeam Kasten annotation (k10.kasten.io/is-snapshot-class: "true").
Note that CSI snapshots are not durable. In particular, CSI snapshots have a namespaced VolumeSnapshot object and a non-namespaced VolumeSnapshotContent object. With the default (and recommended) deletionPolicy, if there is a deletion of a volume or the namespace containing the volume, the cleanup of the namespaced VolumeSnapshot object will lead to the cascading delete of the VolumeSnapshotContent object and therefore the underlying storage snapshot.
Setting deletionPolicy to Delete isn't sufficient either as some storage systems will force snapshot deletion if the associated volume is deleted (snapshot lifecycle is not independent of the volume). Similarly, it might be possible to force-delete snapshots through the storage array's native management interface. Enabling backups together with volume snapshots is therefore required for a durable backup.
Veeam Kasten creates a clone of the original VolumeSnapshotClass with the DeletionPolicy set to 'Retain'. When restoring a CSI VolumeSnapshot, an independent replica is created using this cloned class to avoid any accidental deletions of the underlying VolumeSnapshotContent.
VolumeSnapshotClass Configuration
- Alpha CSI Snapshot API
- Beta CSI Snapshot API
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1alpha1
snapshotter: hostpath.csi.k8s.io
kind: VolumeSnapshotClass
metadata:
annotations:
k10.kasten.io/is-snapshot-class: "true"
name: csi-hostpath-snapclass
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1beta1
driver: hostpath.csi.k8s.io
kind: VolumeSnapshotClass
metadata:
annotations:
k10.kasten.io/is-snapshot-class: "true"
name: csi-hostpath-snapclass
Given the configuration requirements, the above code illustrates a correctly-configured VolumeSnapshotClass for Veeam Kasten. If the VolumeSnapshotClass does not match the above template, please follow the below instructions to modify it. If the existing VolumeSnapshotClass cannot be modified, a new one can be created with the required annotation.
-
Whenever Veeam Kasten detects volumes that were provisioned via a CSI driver, it will look for a VolumeSnapshotClass with Veeam Kasten annotation for the identified CSI driver and use it to create snapshots. You can easily annotate an existing VolumeSnapshotClass using:
$ kubectl annotate volumesnapshotclass ${VSC_NAME} \
k10.kasten.io/is-snapshot-class=trueVerify that only one VolumeSnapshotClass per storage provisioner has the Veeam Kasten annotation. Currently, if no VolumeSnapshotClass or more than one has the Veeam Kasten annotation, snapshot operations will fail.
# List the VolumeSnapshotClasses with Veeam Kasten annotation
$ kubectl get volumesnapshotclass -o json | \
jq '.items[] | select (.metadata.annotations["k10.kasten.io/is-snapshot-class"]=="true") | .metadata.name'
k10-snapshot-class
StorageClass Configuration
As an alternative to the above method, a StorageClass can be annotated
with the following-(k10.kasten.io/volume-snapshot-class: "VSC_NAME").
All volumes created with this StorageClass will be snapshotted by the
specified VolumeSnapshotClass:
$ kubectl annotate storageclass ${SC_NAME} \
k10.kasten.io/volume-snapshot-class=${VSC_NAME}
Migration Requirements
If application migration across clusters is needed, ensure that the VolumeSnapshotClass names match between both clusters. As the VolumeSnapshotClass is also used for restoring volumes, an identical name is required.
CSI Snapshotter Minimum Requirements
Finally, ensure that the csi-snapshotter container for all CSI drivers
you might have installed has a minimum version of v1.2.2. If your CSI
driver ships with an older version that has known bugs, it might be
possible to transparently upgrade in place using the following code.
# For example, if you installed the GCP Persistent Disk CSI driver
# in namespace ${DRIVER_NS} with a statefulset (or deployment)
# name ${DRIVER_NAME}, you can check the snapshotter version as below:
$ kubectl get statefulset ${DRIVER_NAME} --namespace=${DRIVER_NS} \
-o jsonpath='{range .spec.template.spec.containers[*]}{.image}{"\n"}{end}'
gcr.io/gke-release/csi-provisioner:v1.0.1-gke.0
gcr.io/gke-release/csi-attacher:v1.0.1-gke.0
quay.io/k8scsi/csi-snapshotter:v1.0.1
gcr.io/dyzz-csi-staging/csi/gce-pd-driver:latest
# Snapshotter version is old (v1.0.1), update it to the required version.
$ kubectl set image statefulset/${DRIVER_NAME} csi-snapshotter=quay.io/k8scsi/csi-snapshotter:v1.2.2 \
--namespace=${DRIVER_NS}
AWS Storage
Veeam Kasten supports Amazon Web Services (AWS) storage integration, including Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) and Amazon Elastic File System (EFS)
Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) Integration
Veeam Kasten currently supports backup and restores of EBS CSI volumes as well as Native (In-tree) volumes. In order to work with the In-tree provisioner, or to migrate snapshots within AWS, Veeam Kasten requires an Infrastructure Profile. Please refer to AWS Infrastructure Profile on how to create one. Block Mode Exports of EBS volumes use the AWS EBS Direct API.
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) Integration
Veeam Kasten currently supports backup and restores of statically
provisioned EFS CSI volumes. Since statically provisioned volumes use
the entire file system we are able to utilize AWS APIs to take backups.
While the EFS CSI driver has begun supporting dynamic provisioning, it
does not create new EFS volumes. Instead, it creates and uses access
points within existing EFS volumes. The current AWS APIs do not support
backups of individual access points.
However, Veeam Kasten can take backups of these dynamically
provisioned EFS volumes using the
[Shareable Volume Backup and Restore](./shareable-volume.md mechanism).
For all other operations, EFS requires an Infrastructure Profile. Please refer to AWS Infrastructure Profile on how to create one.
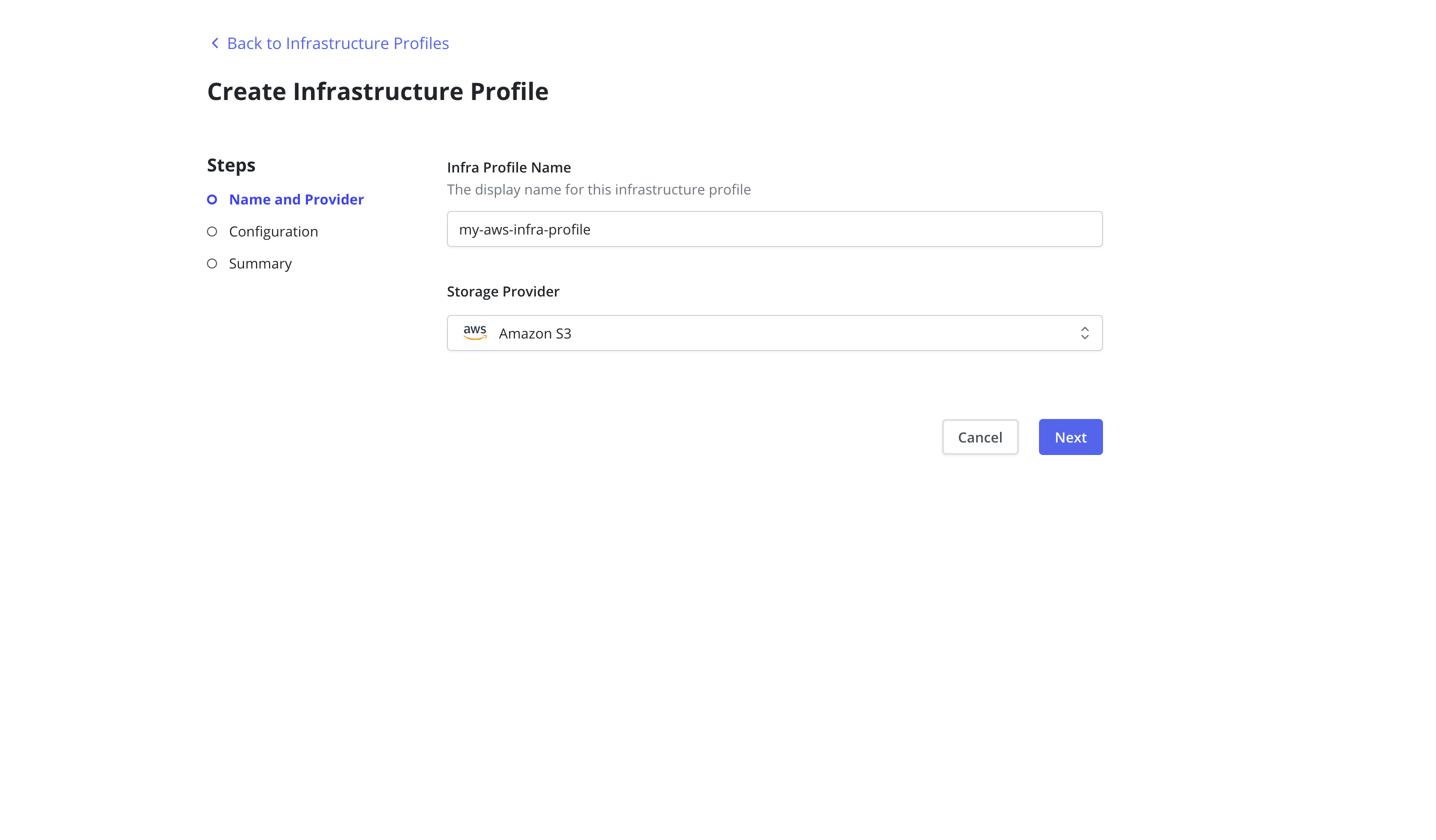
AWS Infrastructure Profile
To enable Veeam Kasten to take snapshots and restore volumes from AWS,
an Infrastructure Profile must be created from the Infrastructure page
of the Profiles menu in the navigation sidebar.
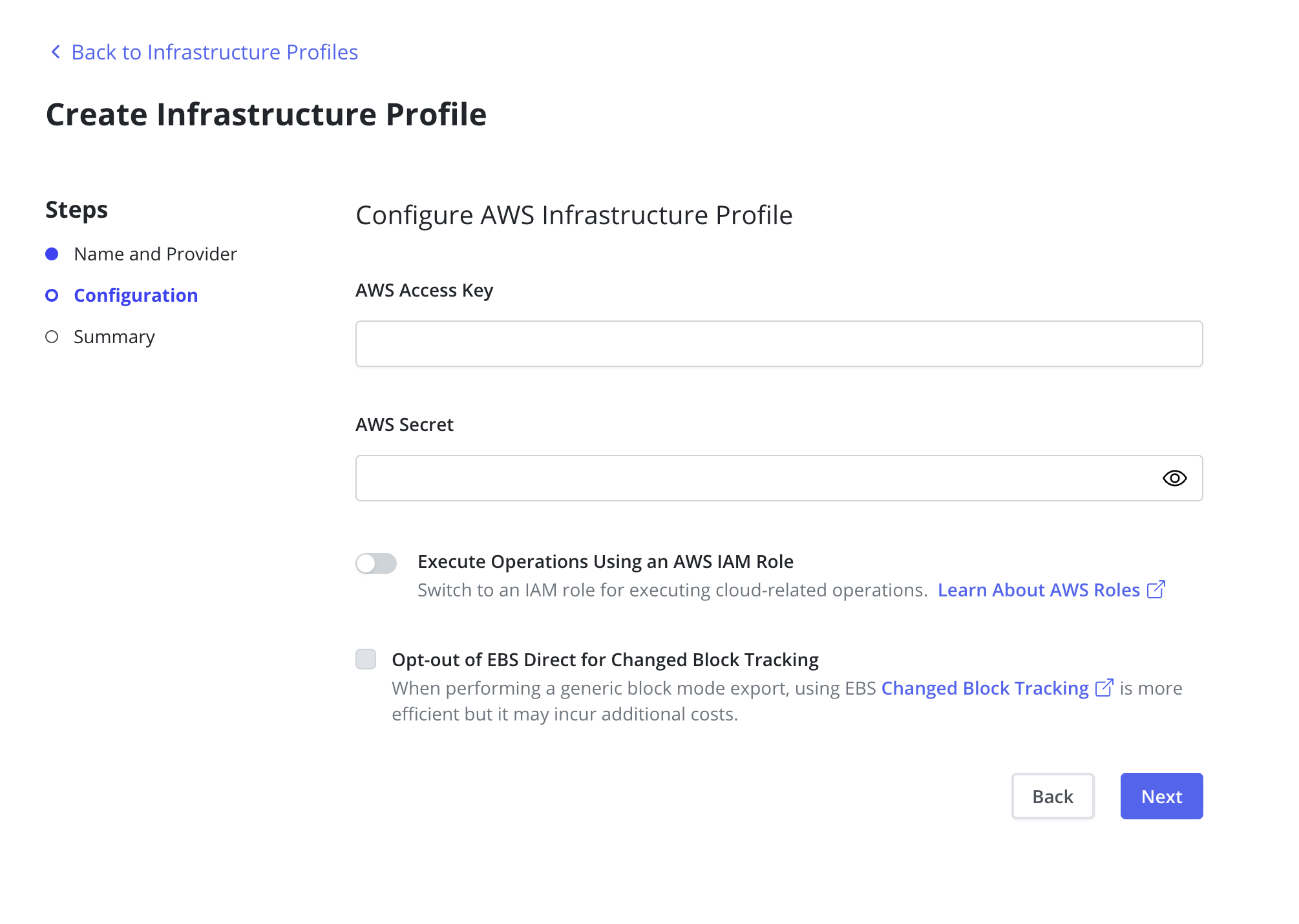
Using AWS IAM Service Account Credentials that Veeam Kasten was installed with is also
possible with the Authenticate with AWS IAM Role checkbox. An
additional AWS IAM Role can be provided if the user requires Veeam
Kasten to assume a different role. The provided credentials are verified
for both EBS and EFS.
Currently, Veeam Kasten also supports the legacy mode of providing AWS credentials via Helm. In this case, an AWS Infrastructure Profile will be created automatically with the values provided through Helm, and can be seen on the Dashboard. This profile can later be replaced or updated manually if necessary, such as when the credentials change.
In future releases, providing AWS credential via Helm will be deprecated.
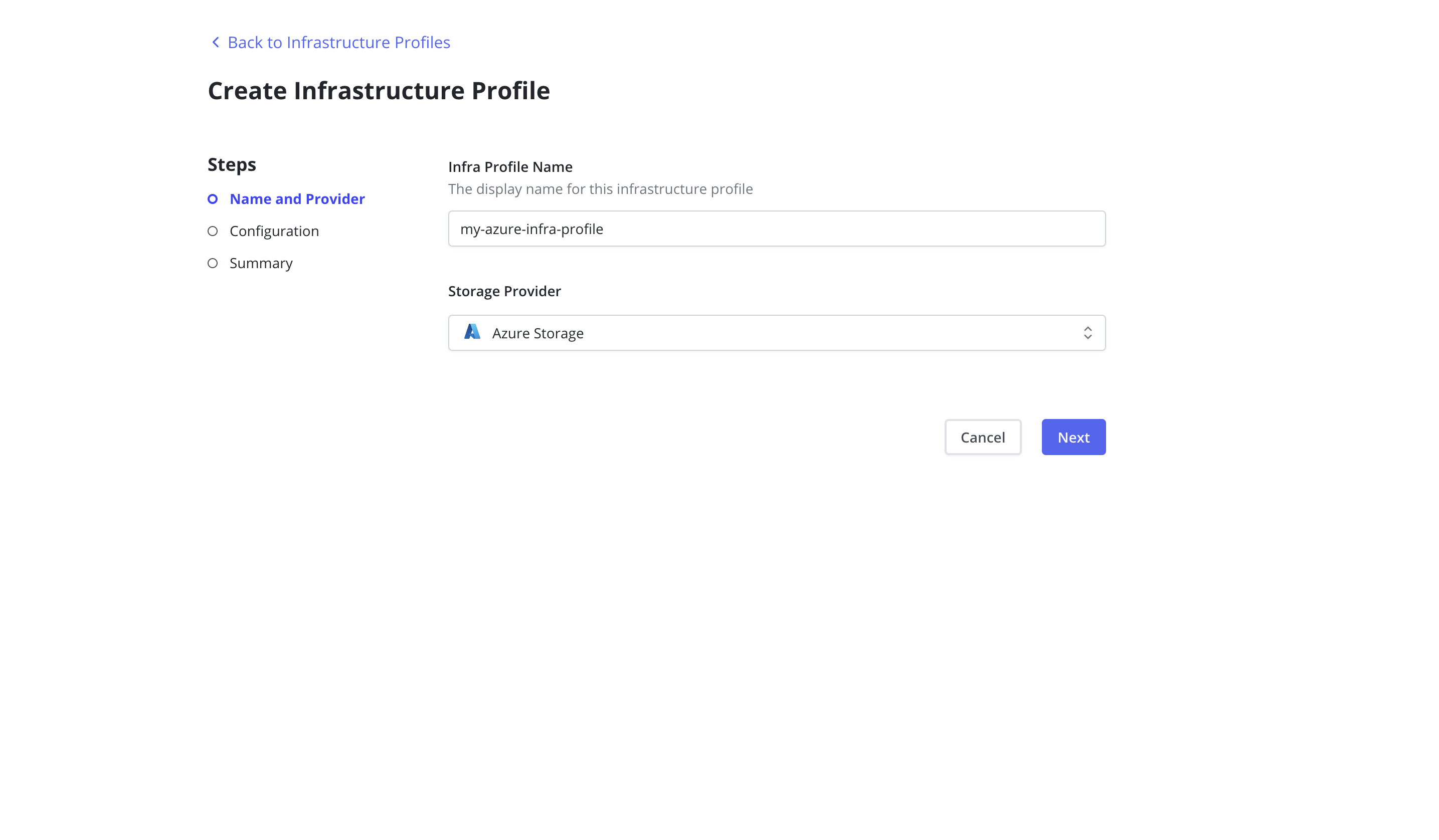
Azure Managed Disks
Veeam Kasten supports backups and restores for both CSI volumes and
in-tree volumes within Azure Managed Disks. To work with the Azure
in-tree provisioner, Veeam Kasten requires the creation of an
Infrastructure Profile from the Infrastructure page of the Profiles
menu in the navigation sidebar.
Veeam Kasten can perform block mode exports with changed block tracking (CBT)
for volumes provisioned using the disk.csi.azure.com CSI driver. This
capability is automatically utilized when the following conditions are met:
- Veeam Kasten includes a valid Azure Infrastructure Profile
- Either the Azure Disk storage class or individual PVC enables Block Mode Exports
- The Azure Disk volume snapshot class enables incremental snapshots, as shown in the example below:
$ kubectl get volumesnapshotclass csi-azuredisk-vsc -o yaml
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1
deletionPolicy: Delete
driver: disk.csi.azure.com
kind: VolumeSnapshotClass
metadata:
annotations:
k10.kasten.io/is-snapshot-class: "true"
snapshot.storage.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
creationTimestamp: "2024-10-28T14:48:50Z"
generation: 1
name: csi-azuredisk-vsc
resourceVersion: "2502"
uid: 9ebec324-0f09-42fa-aace-39440b3184b6
parameters:
incremental: "true" # available values: "true", "false" ("true" by default for Azure Public Cloud, and "false" by default for Azure Stack Cloud)
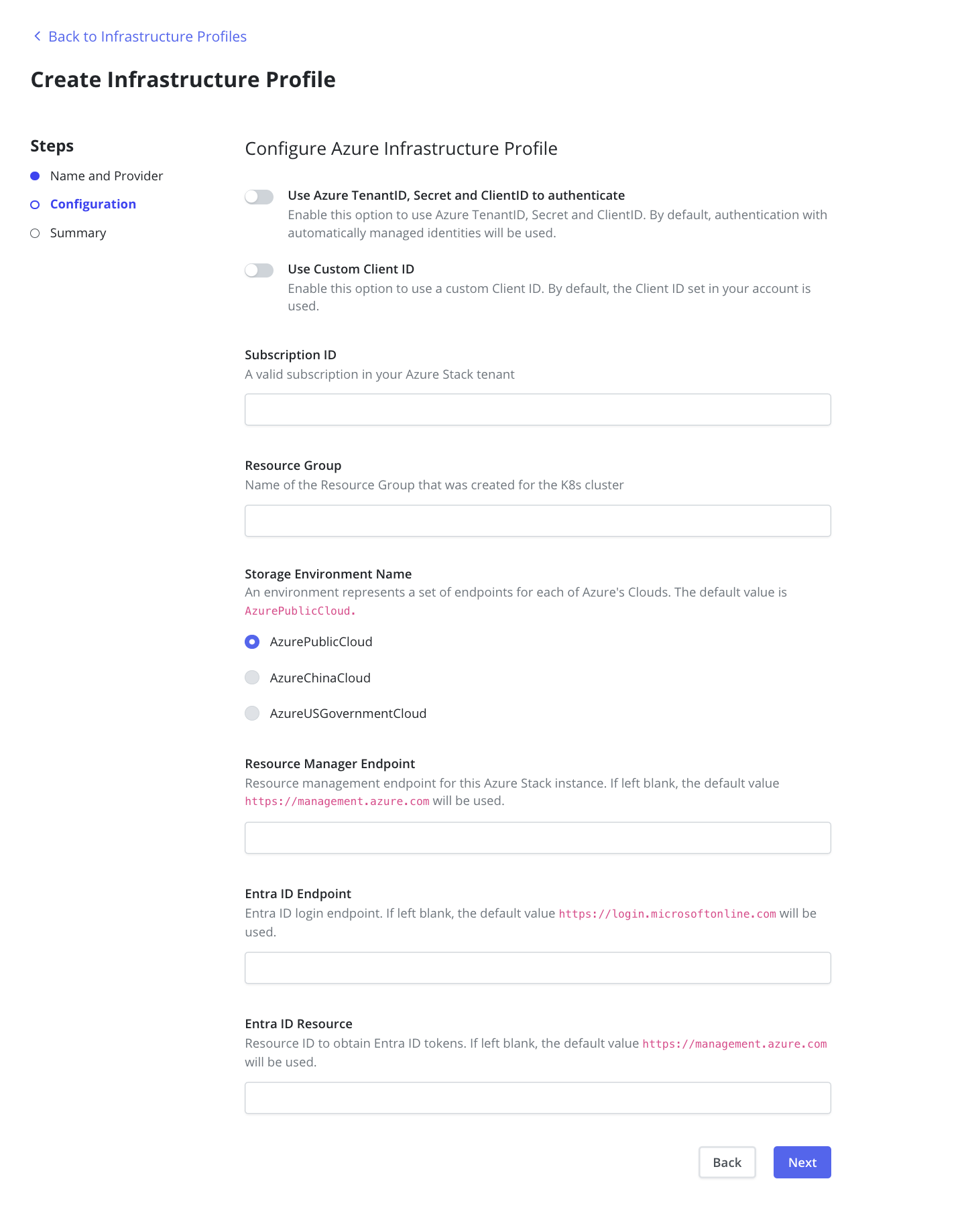
Service Principal
Veeam Kasten supports authentication with Microsoft Entra ID (formerly
Azure Active Directory) with Azure Client Secret credentials, as well as
Azure Managed Identity.
To authenticate with Azure Client Secret credentials, Veeam Kasten
requires Tenant ID, Client ID, and Client Secret.
Managed Identities
If Use Azure TenantID, Secret and ClientID to authenticate is chosen, users will
opt out of using Managed Identity and need to provide their own Tenant ID,
Client Secret and Client ID.
To use Managed Identity but provide a custom Client ID, users can choose
Custom Client ID and provide their own, otherwise the default Managed Identity will be used.
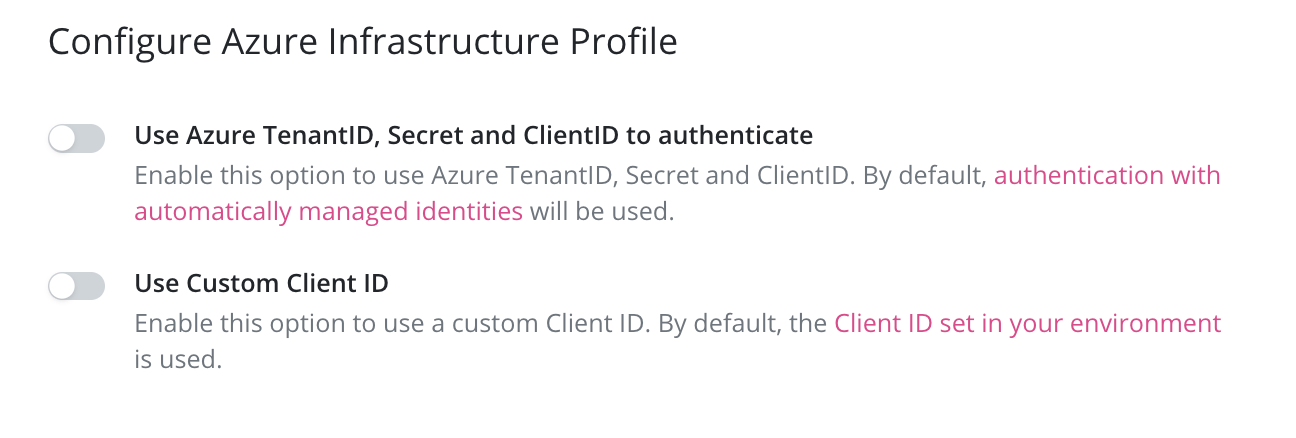
To authenticate with Azure Managed Identity, clusters must have Azure Managed Identity enabled.
Federated Identity
To authenticate with Azure Federated Identity (also known as workload identity), clusters must have Azure Federated Credentials set up. This can only be done via helm. More information can be found here.
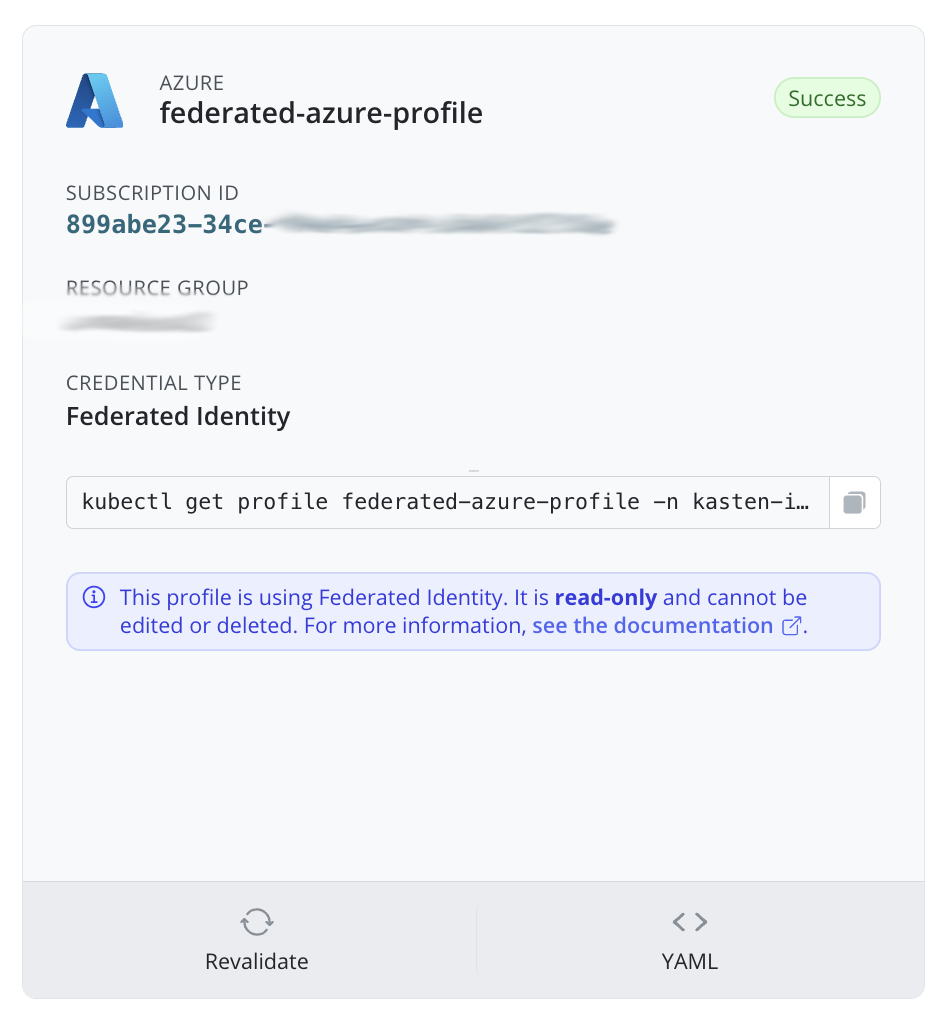
|
Federated Identity is currently only supported on Openshift clusters with version 4.14 and later.
If you are using Federated Identity, you cannot edit or delete the infrastructure profile once created. You can edit or delete by using helm upgrade.
Other Configuration
In addition to authentication credentials, Veeam Kasten also requires
Subscription ID and Resource Group. For information on how to
retrieve the required data, please refer to Installing Veeam Kasten on
Azure.
Additionally, information for Azure Stack such as
Storage Environment Name, Resource Manager Endpoint, AD Endpoint,
and AD Resource can also be specified. These fields are not mandatory,
and default values will be used if they are not provided by the user.
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Storage Environment Name | AzurePublicCloud |
| Resource Manager Endpoint | https://management.azure.com/ |
| AD Endpoint | https://login.microsoftonline.com/ |
| AD Resource | https://management.azure.com/ |
Veeam Kasten also supports the legacy method of providing Azure credentials via Helm. In this case, an Azure Infrastructure Profile will be created automatically with the values provided through Helm, and can be seen on the Dashboard. This profile can later be replaced or updated manually if necessary, such as when the credentials change.
In future releases, providing Azure credentials via Helm will be deprecated.
Pure Storage
For integrating Veeam Kasten with Pure Storage, please follow Pure Storage's instructions on deploying the Pure Storage Orchestrator and the VolumeSnapshotClass.
Once the above two steps are completed, follow the instructions for
Veeam Kasten CSI integration<csi>. In
particular, the Pure VolumeSnapshotClass needs to be edited using the
following commands.
$ kubectl annotate volumesnapshotclass pure-snapshotclass \
k10.kasten.io/is-snapshot-class=true
NetApp Trident
For integrating Veeam Kasten with NetApp Trident, please follow
NetApp's instructions on deploying Trident as a CSI
provider and then follow the
instructions above<csi>.
Google Persistent Disk
Veeam Kasten supports Google Persistent Disk (GPD) storage integration
with both CSI and native (in-tree) drivers. In order to use GPD native
driver, an Infrastructure Profile must be created from the
Infrastructure page of the Profiles menu in the navigation sidebar.
The GCP Project ID and GCP Service Key fields are required. The
GCP Service Key takes the complete content of the service account json
file when creating a new service account.
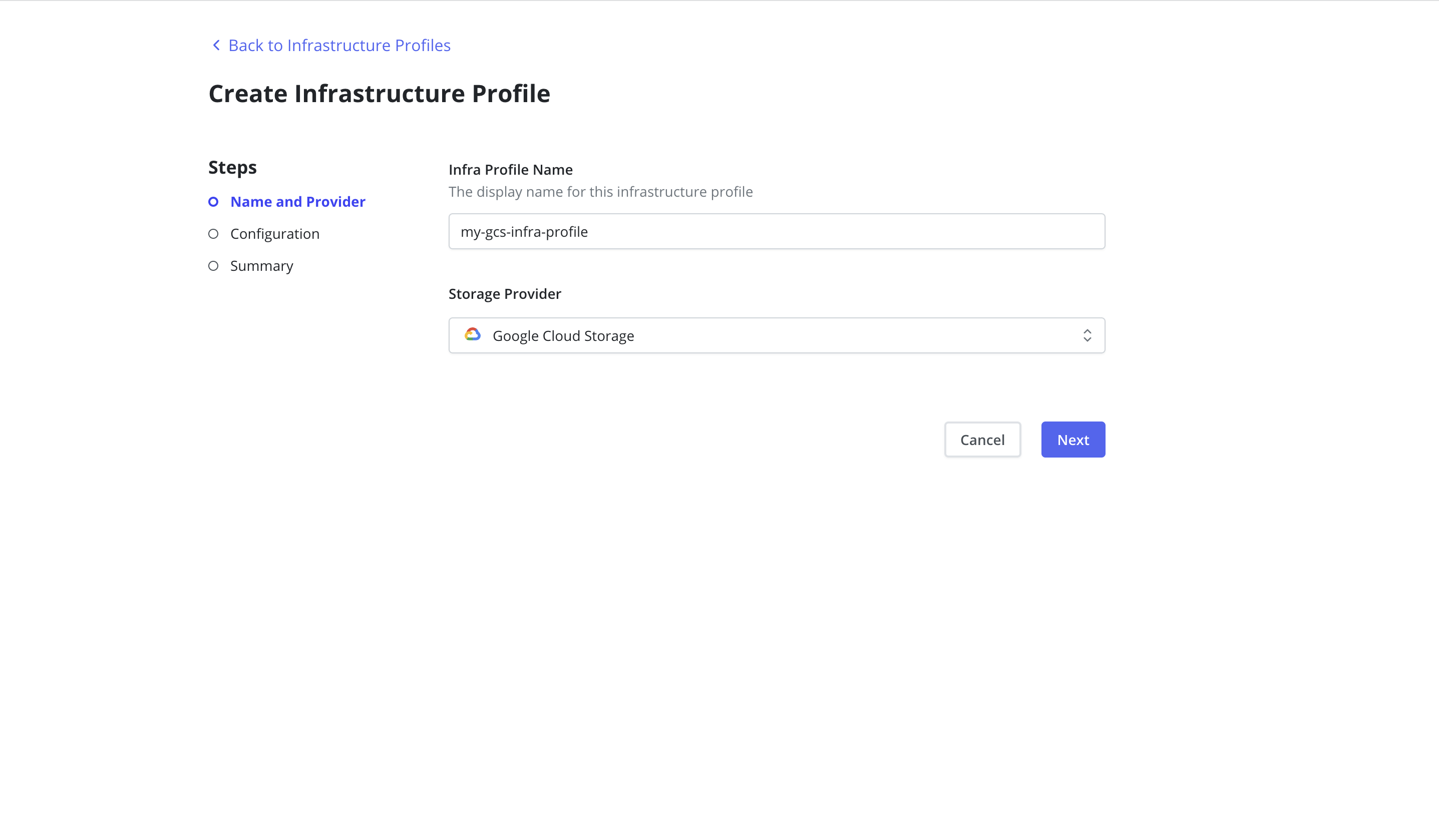
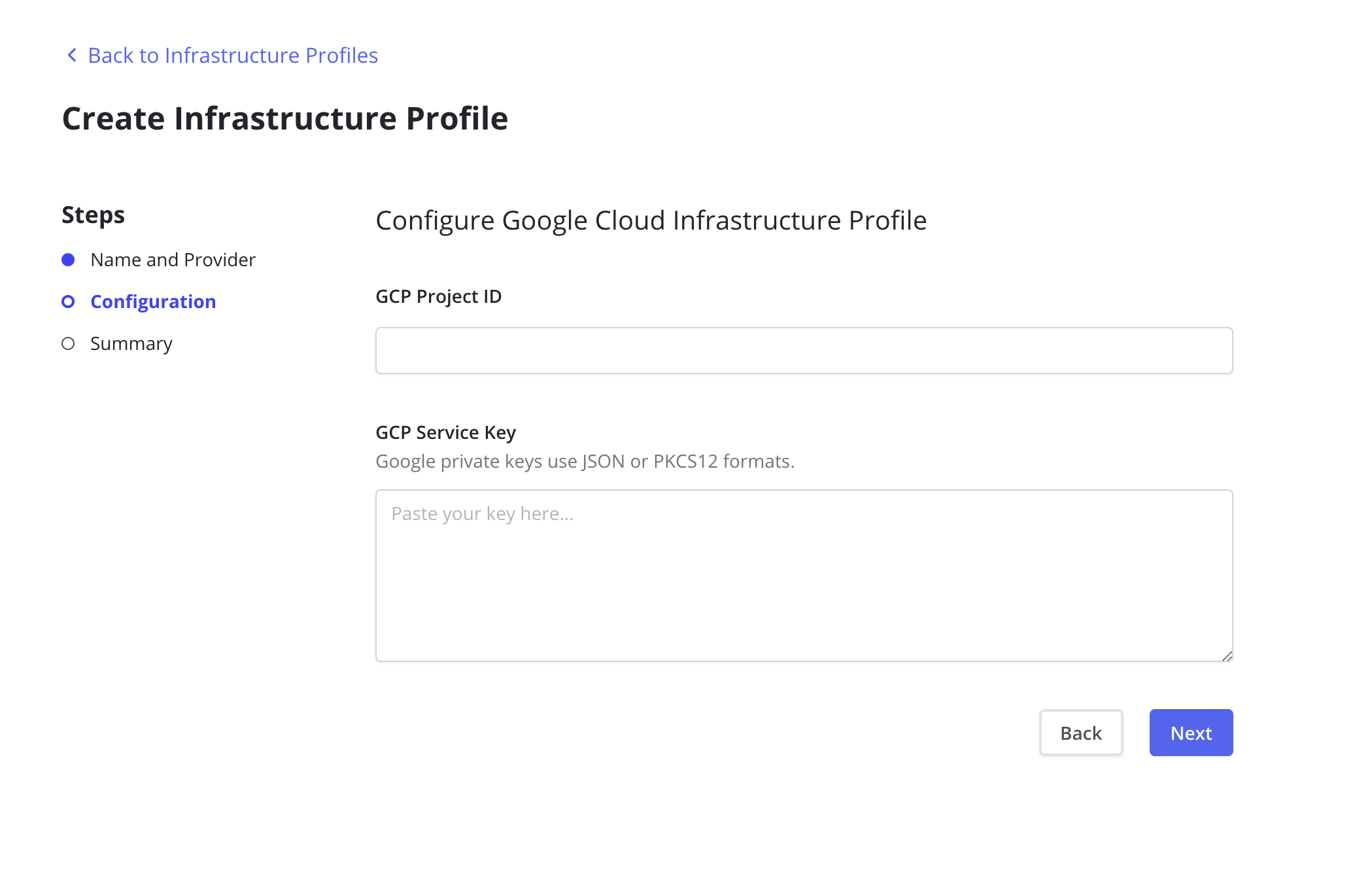
Currently, Veeam Kasten also supports the legacy mode of providing Google credentials via Helm. In this case, a Google Infrastructure Profile will be created automatically with the values provided through Helm, and can be seen on the Dashboard. This profile can later be replaced or updated manually if necessary, such as when the credentials change.
In future releases, providing Google credential via Helm will be deprecated.
Ceph
Veeam Kasten supports Ceph RBD and Ceph FS snapshots and backups via their CSI drivers.
CSI Integration
If you are using Rook to install Ceph, Veeam Kasten only supports Rook v1.3.0 and above. Previous versions had bugs that prevented restore from snapshots.
Veeam Kasten supports integration with Ceph (RBD and FS) via its CSI
interface by following the instructions for
CSI integration<csi>. In particular, the
Ceph VolumeSnapshotClass needs to be edited using the following
commands.
$ kubectl annotate volumesnapshotclass csi-snapclass \
k10.kasten.io/is-snapshot-class=true
Ceph CSI RBD volume snapshots can be exported in block mode with the appropriate annotation on their StorageClass. The Ceph Rados Block Device API can enable direct access to data blocks through the network and provide information on the allocated blocks in a snapshot, which could reduce the size and duration of a backup; however, it is important to note that Changed Block Tracking is not supported for Ceph CSI RBD snapshots. The output of the Veeam Kasten Primer Block Mount Check command indicates if the API will be used:
...
Block mount checker:
StorageClass ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd is annotated with 'k10.kasten.io/sc-supports-block-mode-exports=true'
StorageClass ocs-storagecluster-ceph-rbd is supported by K10 in Block volume mode via vendor APIs (Ceph Rados Block Device)
Snapshots as Shallow Read-Only Volumes (CephFS only)
Veeam Kasten supports the use of snapshots as shallow read-only volumes specifically designed for file systems (FS), particularly for the CephFS CSI driver. Using this feature requires a special StorageClass, which is usually a copy of the regular StorageClass of the CephFS CSI driver, but with the backingSnapshot: "true" option in the parameters section. This StorageClass has to meet the Veeam Kasten requirements for CSI StorageClass configuration. In addition to this, it is necessary to define specific changes (overrides) for the exportData setting within a policy. An illustrative example can be found here: [overrides for exportData setting of
Below is an example of how to specify these overrides for your reference:
exportData:
enabled: true
overrides:
- storageClassName: regular-cephfs-csi-storage-class
enabled: true
exporterStorageClassName: shallow-cephfs-csi-storage-class
Since 'Snapshots as a shallow read-only volumes' feature requires a read-only mount of the Snapshot PVC during the Export phase, support for read-only mount has to be enabled:
$ kubectl annotate storageclass shallow-cephfs-csi-storage-class \
k10.kasten.io/sc-supports-read-only-mount="true"
An Openshift cluster requires preserving SELinuxLevel of source namespace to Kanister Pod during the Export phase. This functionality always enabled in Veeam Kasten, thus additional actions are not required.
Cinder/OpenStack
Veeam Kasten supports snapshots and backups of OpenStack's Cinder block storage.
To enable Veeam Kasten to take snapshots, an OpenStack Infrastructure
Profile must be created from the Infrastructure page of the Profiles
menu in the navigation sidebar.
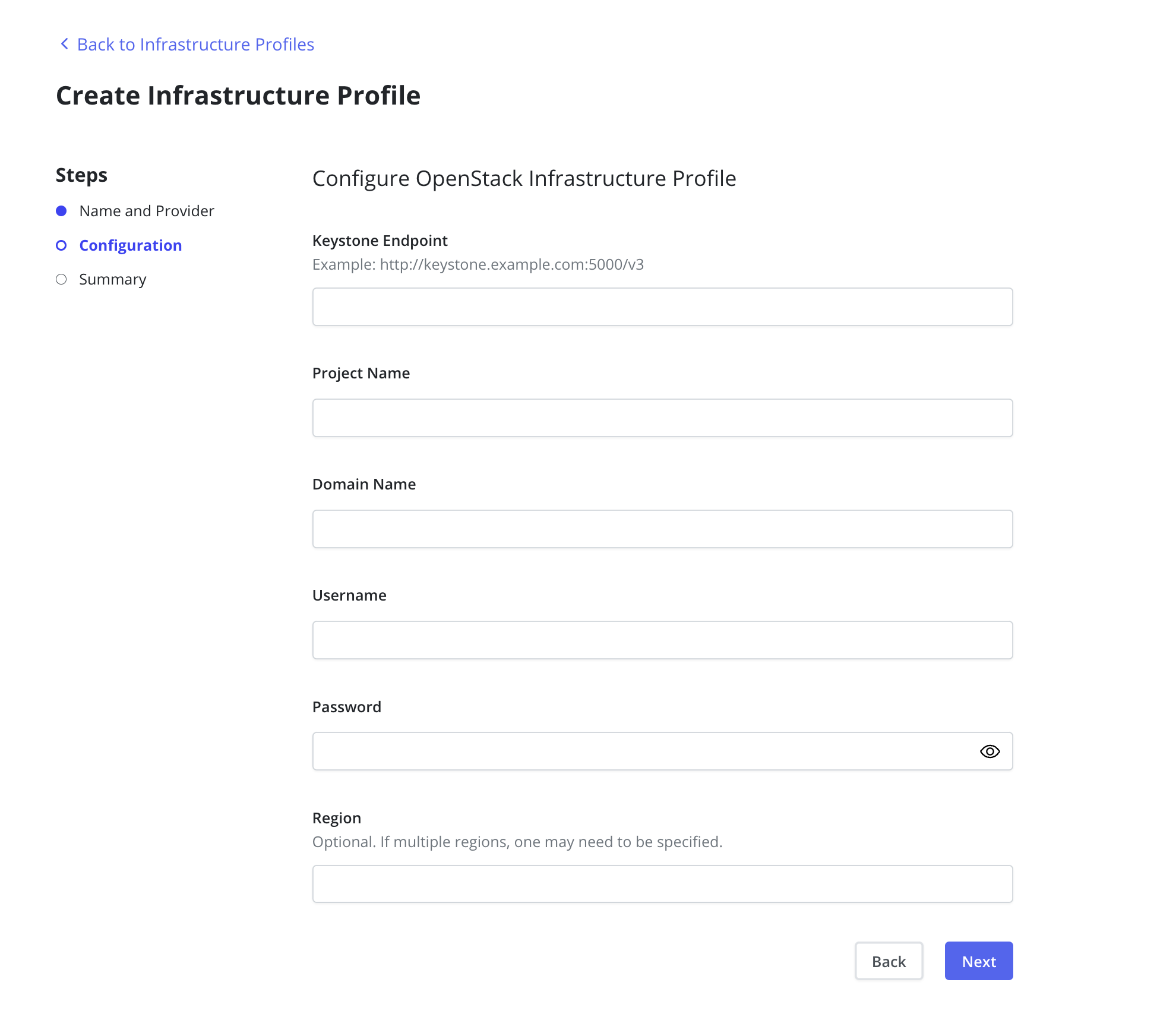
The Keystone Endpoint, Project Name, Domain Name, Username and
Password are required fields. If the OpenStack environment spans
multiple regions then the Region field must also be specified.
vSphere
Veeam Kasten supports vSphere storage integration with PersistentVolumes provisioned using the vSphere CSI Provisioner.
Currently, backup and restore operations are not supported for RWX/ROX volumes provisioned using vSAN File Services.
The available functionality varies by the type of cluster infrastructure used and is summarized in the table below:
| vSphere with Tanzu [1] | Other Kubernetes infrastructures [1] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| vSphere | Supported versions | 7.0 U3 or higher | 7.0 U1 or higher |
| vCenter access required [2] | Required | Required | |
| Export | Export in filesystem mode | Not Supported [3] | Supported |
| Export in block mode [4] | To an Object Storage Location, an NFS File Storage Location or a Veeam Repository [5] | To an Object Storage Location, an NFS File Storage Location or a Veeam Repository [5] | |
| Restore | Restore from a snapshot | Not Supported [3] | Supported |
| Restore from an export (any mode) | Supported | Supported | |
| Instant Recovery restore | Not Supported [3] | From a Veeam Repository | |
| Import | Import a filesystem mode export | Supported | Supported |
| Import a block mode export | From an Object Storage Location, an NFS File Storage Location or a Veeam Repository [5] | From an Object Storage Location, an NFS File Storage Location or a Veeam Repository [5] | |
- vSphere with Tanzu supervisor clusters and VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid management clusters are not supported.
- Access to vCenter is required with all types of cluster infrastructures as Veeam Kasten directly communicates with vSphere to snapshot a First Class Disk (FCD), resolve paravirtualized volume handles, set tags and access volume data with the VMware VDDK API.
- The guest clusters of vSphere with Tanzu use paravirtualized PersistentVolumes. These clusters do not support the static provisioning of a specific FCD from within the guest cluster itself. This disables Veeam Kasten's ability to restore applications from their local snapshots, Instant Recovery and the ability to export snapshot data in filesystem mode.
- Block mode snapshot exports are available in all types of vSphere cluster infrastructures. Snapshot content is accessed at the block level directly through the network using the VMware VDDK API. Enable changed block tracking on the VMware cluster nodes to reduce the amount of data transferred during export. See this Veeam Kasten knowledge base article for how to do so in vSphere with Tanzu guest clusters.
- Block mode snapshot exports can be saved in an Object Storage Location, an NFS File Storage Location or a Veeam Repository.
A vSphere Infrastructure Profile must be created from the
Infrastructure page of the Profiles menu in the navigation sidebar
to identify the vCenter server.
The vCenter Server is required and must be a valid IP address or hostname
that points to the vSphere infrastructure.
The vSphere User and vSphere Password fields are also required.
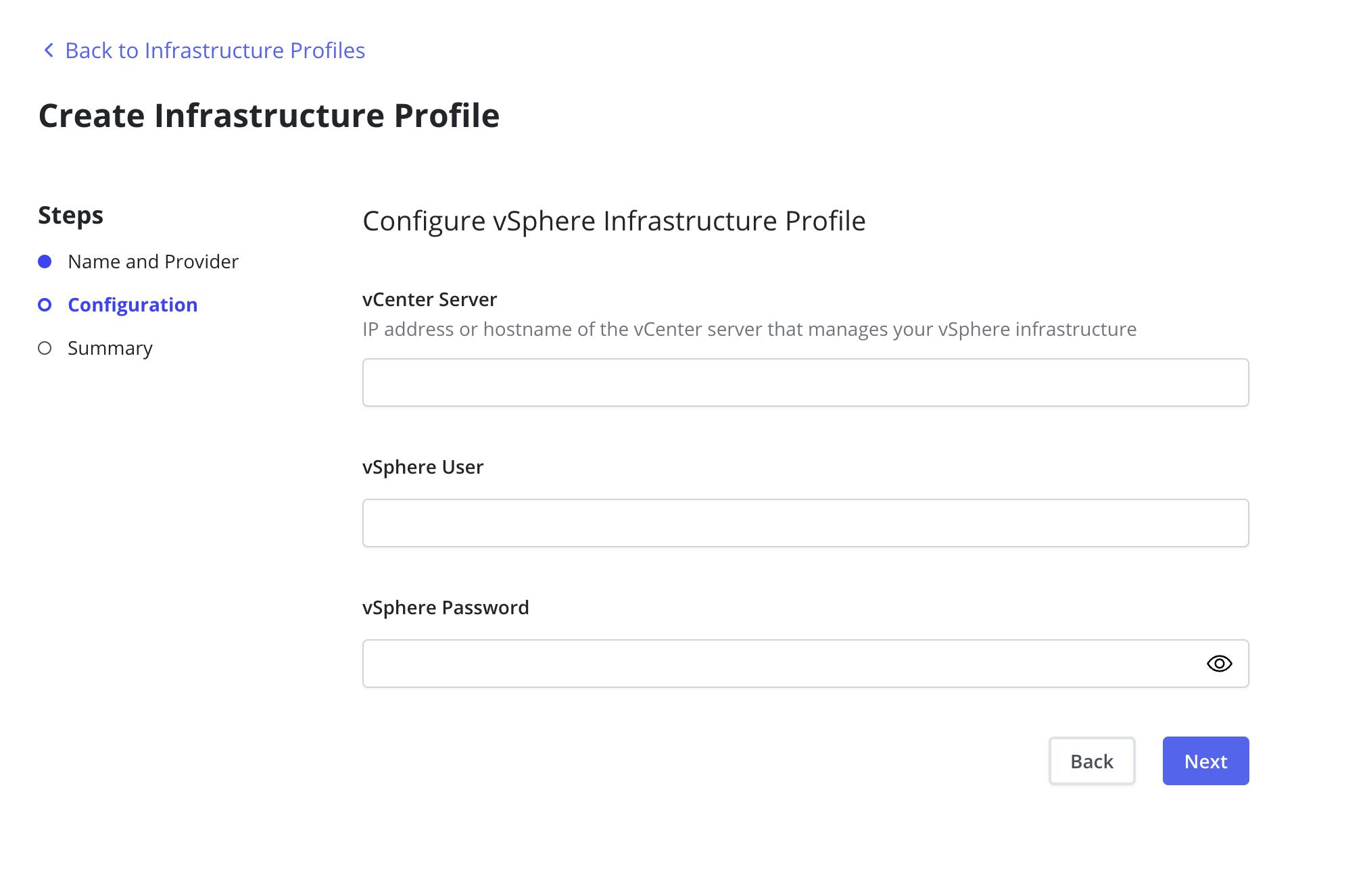
If vSphere credentials are provided during the installation of Veeam Kasten (Installing Veeam Kasten on VMware vSphere) those parameters will be ignored in favor of the credentials contained in the Infrastructure profile.
s:::info Note
It is recommended that a dedicated user account be created for Veeam Kasten. To authorize the account, create a role with the following privileges (for 7.0.x and 8.0.x):
-
Datastore
Privileges(7.0
/
8.0)
- Allocate space
- Browse datastore
- Low level file operations
-
Global Privileges
(7.0
/
8.0)
- Disable methods
- Enable methods
- Licenses
-
Virtual Machine Snapshot Management Privileges
(7.0
/
8.0)
- Create snapshot
- Remove snapshot
- Revert to snapshot
-
Cryptographic operations
(8.0)
- Decrypt
vSphere with Tanzu clusters require the following additional privilege to resolve paravirtualized volume handles:
Also for vSphere with Tanzu, assign the can edit role to the custom user in the vSphere Namespace using the following UI path:
- Workload Management > Namespaces > Select the namespace associated with the TKG service > Permissions > Add (assign [can edit] role)
Assign this role to the dedicated Veeam Kasten user account on the following objects:
- The root vCenter object
- The datacenter objects (propagate down each subtree to reach datastore and virtual machine objects) :::
There is an upper limit on the maximum number of snapshots for a VMware Kubernetes PersistentVolume. Refer to this or more recent VMware knowledge base articles for the limit and for recommendations on the number of snapshots to maintain. A Veeam Kasten backup policy provides control over the number of local Veeam Kasten restore points retained, and by implication, the number of local snapshots retained. A Veeam Kasten backup and export policy allows separate retention policies for local and exported Veeam Kasten restore points. It is possible to set a 0 local restore point retention value (i.e. no local snapshots are retained), as long as a non-zero exported restore point retention value is set; doing so does not adversely impact the ability to use incremental block mode exports with changed block tracking.
The Veeam Kasten default timeout for vSphere snapshot related operations
may be too short if you are dealing with very large volumes. If you
encounter timeout errors then adjust the vmWare.taskTimeoutMin Helm
option accordingly.
You may observe that an application's PersistentVolumes do not get deleted even if their Reclaim Policy is Delete. This can happen when using Veeam Kasten to restore an application in the same namespace or when deleting or uninstalling an application previously backed up by Veeam Kasten.
This is because the VMware CSI driver fails in the deletion of PersistentVolumes containing snapshots: a VMware snapshot is embedded in its associated FCD volume and does not exist independent of this volume, and it is not possible to delete an FCD volume if it has snapshots. The VMware CSI driver leaves such PersistentVolumes in the Released state with a "failed to delete volume" warning (visible with kubectl describe). You may also see errors flagged for this operation in the vCenter GUI. The driver re-attempts the deletion operation periodically, so when all snapshots get deleted the PersistentVolume will eventually be deleted. One can also attempt to manually delete the PersistentVolume again at this time.
When Veeam Kasten restores an application in the same namespace from some restore point, new Kubernetes PersistentVolume objects (with new FCD volumes) are created for the application. However, any restore point that involves local snapshots will now point into FCD volumes associated with PersistentVolume objects in the Released state! Deletion of these Veeam Kasten restore points (manually or by schedule) will delete the associated FCD snapshots after which the PersistentVolume objects and their associated FCD volumes will eventually be released.
When uninstalling or deleting an application, do not force delete Kubernetes PersistentVolume objects in the Released state as this would orphan the associated FCD volumes! Instead, use the vCenter GUI or a CLI tool like govc to manually delete the snapshots.
Portworx
Apart from CSI-level support, Veeam Kasten also directly integrates with the Portworx storage platform.
To enable Veeam Kasten to take snapshots and restore volumes from
Portworx, an Infrastructure Profile must be created from the
Infrastructure page of the Profiles menu in the navigation sidebar.
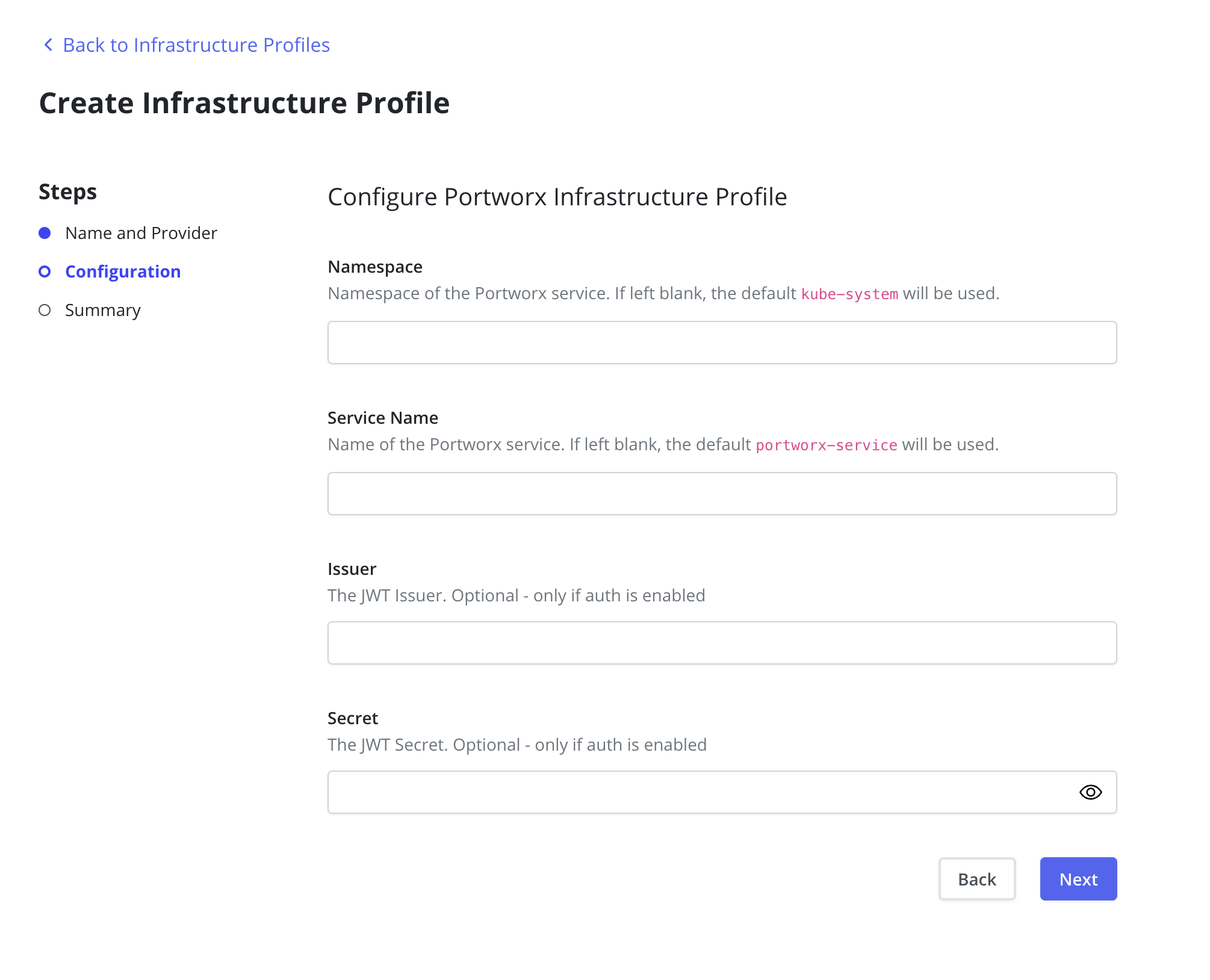
The Namespace and Service Name fields are used to determine the
Portworx endpoint. If these fields are left blank the Portworx defaults
of kube-system and portworx-service will be used respectively.
In an authorization-enabled Portworx setup, the Issuer and Secret
fields must be set. The Issuer must represent the JWT issuer. The
Secret is the JWT shared secret, which is represented by the Portworx
environment variable-PORTWORX_AUTH_JWT_SHAREDSECRET. Refer to
Portworx
Security
for more information.
Veeam Backup
A Veeam Repository can be used as the destination for exported snapshot data from persistent volumes provisioned by the vSphere CSI provider in supported vSphere clusters. See the Integration with Veeam Backup Repositories for Kasten K10 Guide for additional details, including the Veeam user account permissions needed, network ports used and licensing information.
A
Veeam Repository Location Profile must be created to identify the desired repository on a
particular Veeam Backup server (immutable repositories are also
supported, refer to
the setup instructions for more details), A Veeam Repository can only store the
image based volume data from the backup, so a policy which uses a Veeam
Repository location profile will always be used in conjunction with
another location profile that will be used to store the remaining data
in a Veeam Kasten restore point.
A Veeam Repository Location Profile cannot be used as a destination for Kanister actions in a Backup policy.
A Veeam Backup Policy will be created in the Veeam Backup server for each distinct Veeam Kasten protected application and Veeam Kasten backup and export policy pair encountered when the Veeam Kasten backup and export policy is executed. The Veeam Kasten catalog identifier is added to the name to ensure uniqueness across multiple clusters that back up to the same Veeam Backup server.
Data from a manual (i.e. not associated with a Veeam Kasten backup and
export policy) export of an application's volumes is associated with a
fixed policy called Kasten K10 Manual Backup and is saved as a
VeeamZIP backup.
Veeam Kasten will delete any Veeam restore point associated with a Veeam Kasten restore point being retired.
Import and restoration of Veeam Kasten restore points that contain snapshot data exported to a Veeam Repository is possible in supported vSphere clusters using volumes provisioned by the vSphere CSI driver. As Veeam Kasten restore points are not saved in the Veeam Repository the import action is actually performed on the location profile that contains the Veeam Kasten restore point being imported. A Veeam Repository Location Profile Veeam Kasten object with the same name as that used on the exporting system must be present in the importing system and will be referenced during the restore action.
Snapshot data is accessed in block mode directly through the VMware VDDK API. If change block tracking is enabled in the VMware cluster nodes, Veeam Kasten will send incremental changes to the Veeam Backup Server if possible; if incremental upload is not possible a full backup will be done each export. Regardless, Veeam Kasten will convert Veeam restore points into a synthetic full to satisfy Veeam Kasten retirement functionality.
Instant Recovery
Instant Recovery will get an exported restore point up and running much faster than a regular restore. This feature requires vSphere 7.0.3+ and a Veeam Backup server version V12 or higher. This is not supported on vSphere with Tanzu clusters at this time. Before using Instant Recovery, you should ensure that all Storage Classes in your Kubernetes clusters are configured to avoid placing new volumes in the Instant Recovery datastore. Please see this Knowledge Base article for recommendations on Storage Classes for use with Instant Recovery.
When a Veeam Kasten Instant Recovery is triggered, rather than creating volumes and populating them with data from VBR, Veeam Kasten asks the Veeam Backup server to do an Instant Recovery of the FCDs (vSphere First Class Disks) that are needed and then creates PVs that use those FCDs. The FCDs exist in a vPower NFS datastore created by the Veeam Backup server and attached to the vSphere cluster hosting the Kubernetes cluster.
Once the Instant Recovery has completed, the application will be running using the Veeam Backup server storage. At that point, the virtual disks will be migrated into their permanent home with no interruption in service. The application will not see any differences in how it is using the storage and all of the pods using the disks will continue operating without any restarts. The migration will start automatically after the Instant recovery process completes.
Currently Instant Recovery is only supported for Restore Actions, not Restore Policies. To use Instant Recovery, select the Enable Instant Recovery checkbox (this will only appear if all compatibility criteria are met) or set the InstantRecovery property in the RestoreAction spec.
All restore features are supported with Instant Recovery.
