Operator based Installation
K10 Operator Editions
Kasten K10 (Free) : Free edition of K10 for use in clusters up to 10 nodes
Kasten K10 (Enterprise - PAYGO) : Enterprise edition of K10, billed per usage of node-hours
Kasten K10 (Enterprise - Term): Enterprise edition of K10 intended to be used with a term license
Pre-Flight Checks
Assuming that your default oc context is pointed to the cluster you want to install K10 on, you can run pre-flight checks by deploying the primer tool. This tool runs in a pod in the cluster and does the following:
Validates if the Kubernetes settings meet the K10 requirements.
Catalogs the available StorageClasses.
If a CSI provisioner exists, it will also perform a basic validation of the cluster's CSI capabilities and any relevant objects that may be required. It is strongly recommended that the same tool be used to also perform a more complete CSI validation using the documentation here.
Note that this will create, and clean up, a ServiceAccount and ClusterRoleBinding to perform sanity checks on your Kubernetes cluster.
Run the following command to deploy the the pre-check tool:
$ curl https://docs.kasten.io/tools/k10_primer.sh | bash
Prerequisites
You need to create the project where Kasten will be installed. By default, the documentation uses kasten-io.
oc new-project kasten-io \
--description="Kubernetes data management platform" \
--display-name="Kasten K10"
K10 assumes that the default storage class is backed by SSDs or similarly fast storage media. If that is not true, please modify the installation values to specify a performance-oriented storage class.
global:
persistence:
storageClass: <storage-class-name>
K10 Install
Select the OperatorHub from the Operators Menu, search for Kasten. Select either the Certified Operator, or Marketplace version depending on the requirements
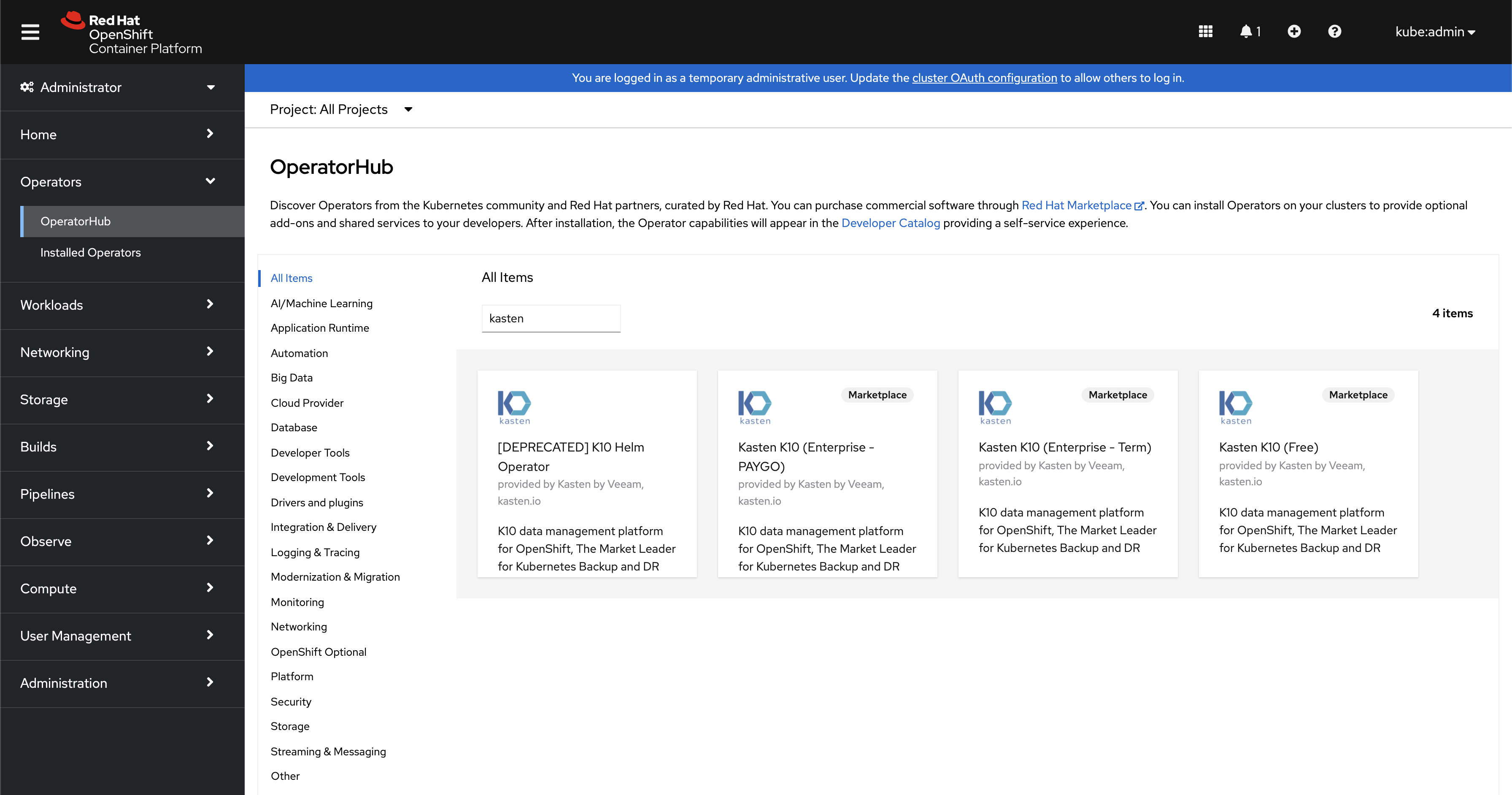
To begin the installation, simply click
Install
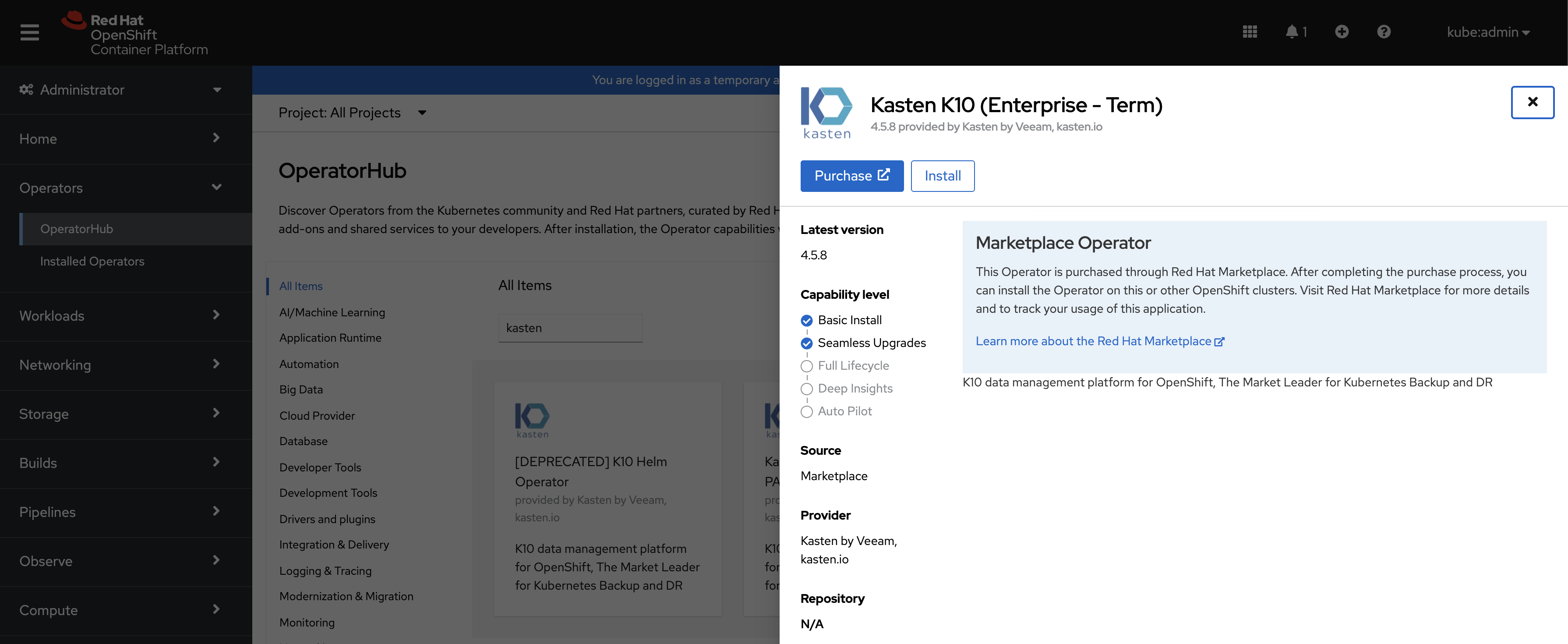
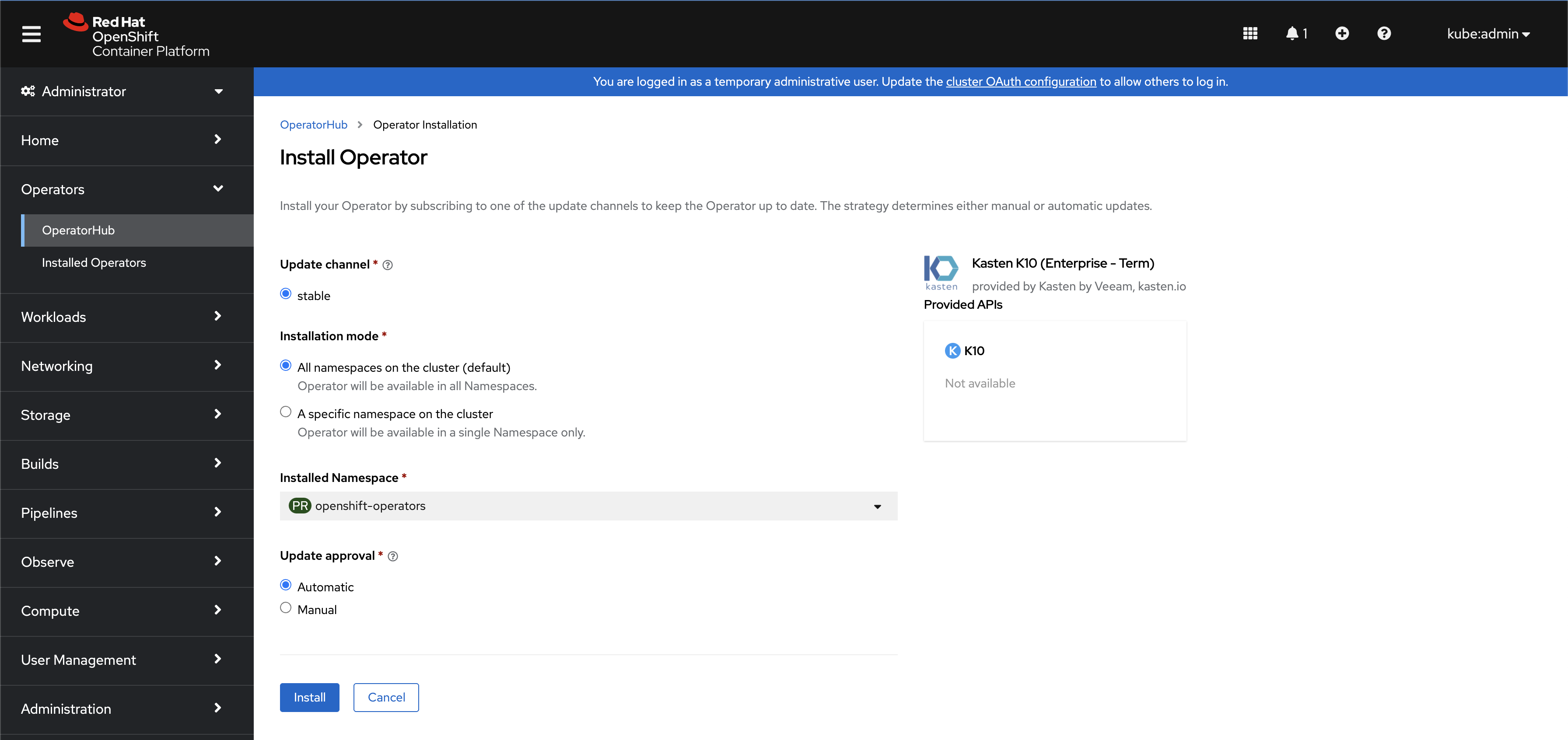
Next, set the channel to stable and installation mode to
A specific namespace on the cluster. Choose thekasten-ioproject created in an earlier step.
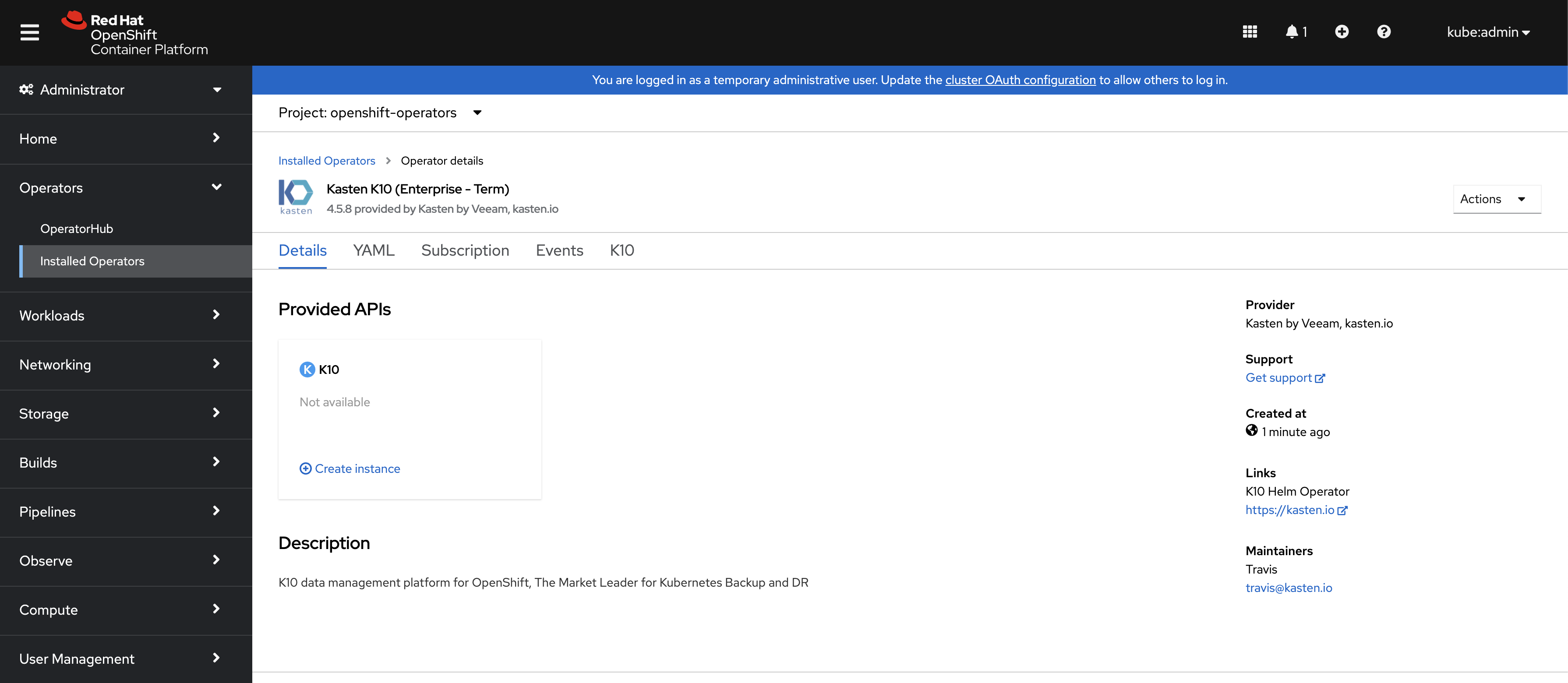
Once installed, a K10 instance can be created by clicking
Create Instancein the operator details page.
The default installation can be done through either the
Form VieworYAML View. There are no changes needed to install by default.
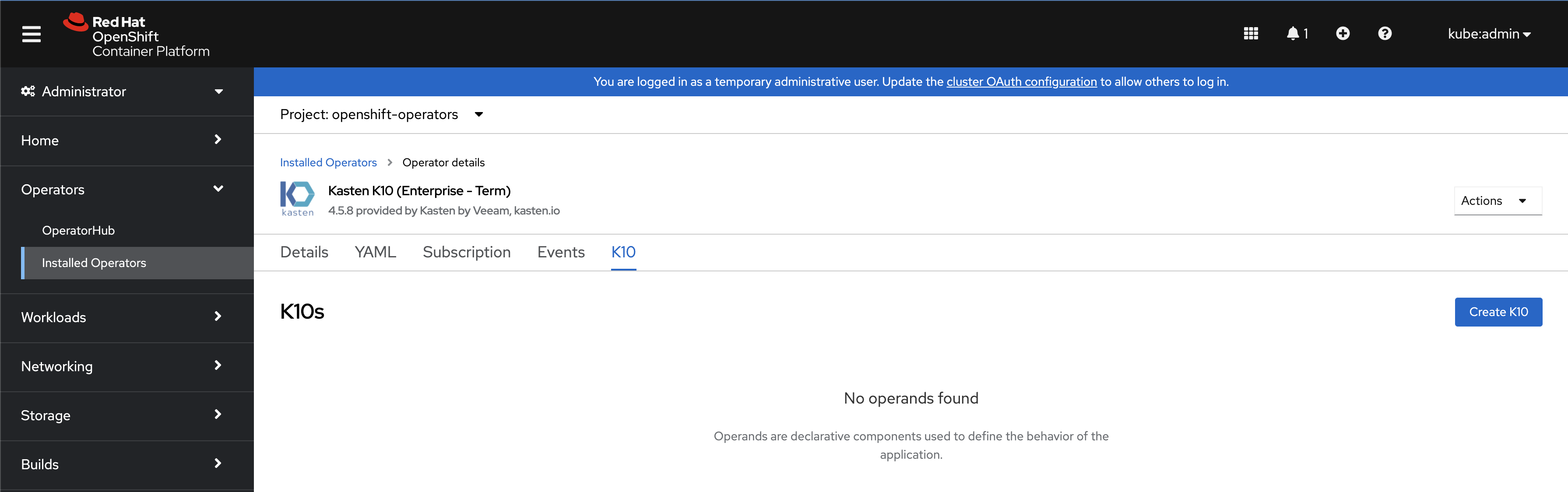
Offline Operator Install
Note
Only K10 Operator Editions "Kasten K10 (Free)" and "Kasten K10 (Enterprise - Term)" are supported in disconnected environments.
Create a filtered RedHat marketplace index image in the private registry
Log into the RedHat registry and the private registry. The private registry is the registry disconnected cluster has access to.
$ docker login registry.redhat.io
$ podman login <private registry>
Prune the index image to include K10 operator(s).
The steps below are using the K10 operators from
registry.redhat.io/redhat/redhat-marketplace-index:v4.9.
$ opm index prune -f registry.redhat.io/redhat/redhat-marketplace-index:v4.9 \
-p k10-kasten-operator-rhmp,k10-kasten-operator-term-rhmp \
-t <private registry>/redhat-marketplace-index:v4.9 \
-c docker
Push the pruned index image to the private registry
$ docker push <private registry>/redhat-marketplace-index:v4.9
Create a pull secret with RedHat and private registry credentials
Follow the steps in Configuring credentials that allow images to be mirrored to create an image registry credentials file that allows mirroring images to the private registry.
Mirror the operator images to the private registry
$ REG_CREDS=pull-secret.json # path to pull secret file created in step 2
$ oc adm catalog mirror <private registry>/redhat-marketplace-index:v4.9 \
<private registry>/olm-mirror -a ${REG_CREDS}
This copies the operator images from RedHat to the local registry. This also creates a manifest directory which is used in the next two steps.
Example output:
...
info: Mirroring completed in 4.61s (0B/s)
no digest mapping available for <private registry>/redhat-marketplace-index:v4.9, skip writing to ImageContentSourcePolicy
wrote mirroring manifests to <path of manifest directory>
Create an ImageContentSourcePolicy in the disconnected cluster
Create an ImageContentSourcePolicy object using the
imageContentSourcePolicy.yaml file in the manifests directory created
in step 3.
$ oc create -f <path to manifests dir>/imageContentSourcePolicy.yaml
Create a CatalogSource in the disconnected cluster
Create a CatalogSource object using the catalogSource.yaml file in the
manifests directory created in step 3.
$ oc create -f <path to manifests dir>/catalogSource.yaml
catalogSource.yaml can be updated to specify a catalog display name as the
example below.
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: CatalogSource
metadata:
name: test-catalog
namespace: openshift-marketplace
spec:
image: <catalog image>
sourceType: grpc
displayName: Offline Catalog
publisher: Local Publisher
updateStrategy:
registryPoll:
interval: 30m
Optionally, default catalog sources can be removed with the command below.
$ oc patch OperatorHub cluster --type json \
-p '[{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/disableAllDefaultSources", "value": true}]'
Verify the package manifest
$ oc get packagemanifest -n openshift-marketplace
NAME CATALOG AGE
k10-kasten-operator-term-rhmp Test Catalog 10m
k10-kasten-operator-rhmp Test Catalog 10m
Install the operators via the operator hub
K10 operators can be now installed from the operator hub.
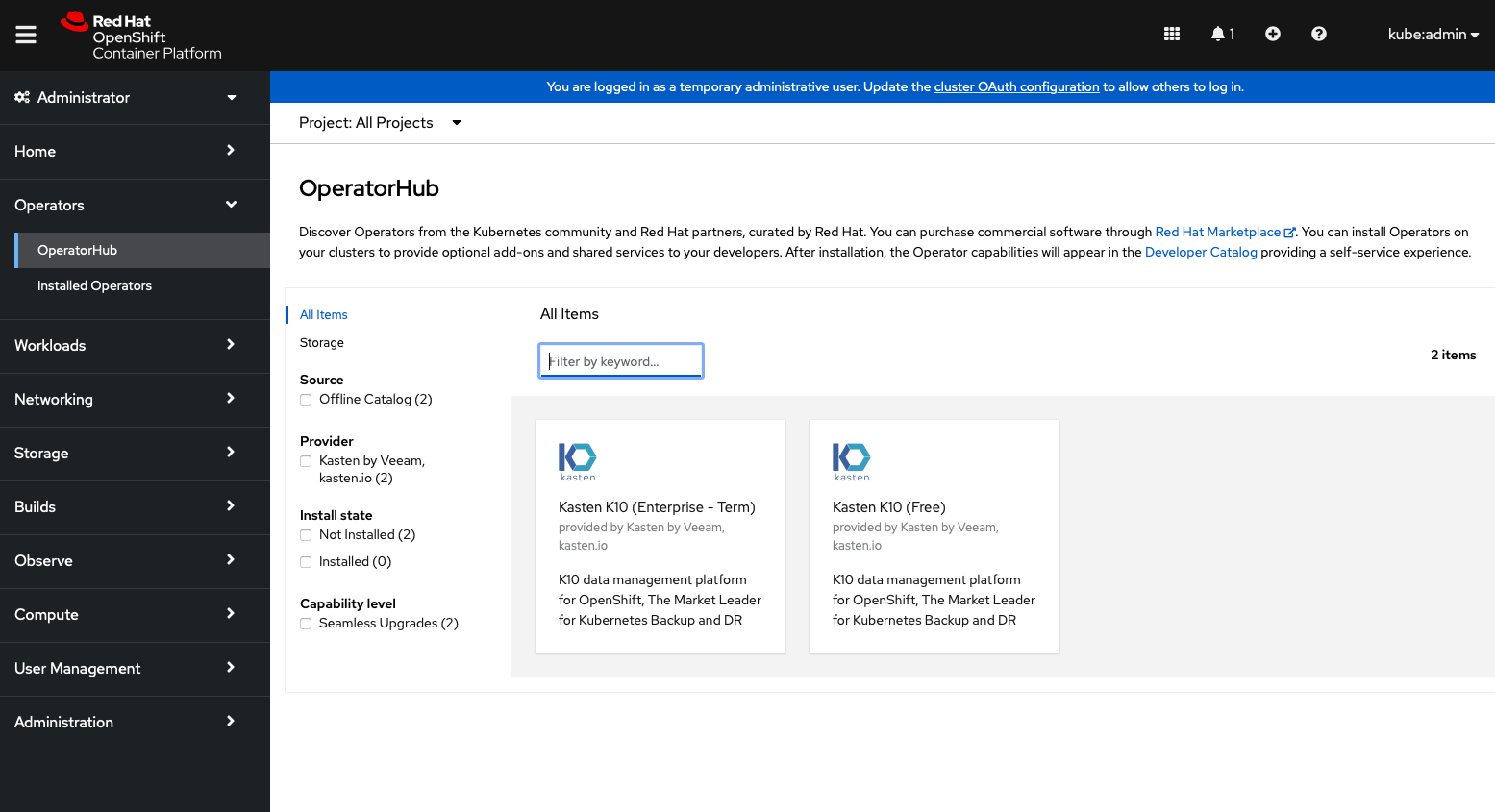
Follow steps under operator install to continue installing K10.
Other Installation Options
For a complete list of installation options please visit our advanced installation page.
Note
After installing the "Kasten K10 (Enterprise - PAYGO)" edition, if the warning message "Unable to validate Red Hat Marketplace license" is displayed on the K10 dashboard, please verify the cluster is registered with Red Hat Marketplace and the Red Hat Marketplace Operator is installed, and then re-install K10
OpenShift on AWS
When running OpenShift on AWS, please configure these policies before running the install command below.
$ helm install k10 kasten/k10 --namespace=kasten-io \
--set scc.create=true \
--set secrets.awsAccessKeyId="${AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID}" \
--set secrets.awsSecretAccessKey="${AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY}"
OpenShift and CSI
Note
The feature flag mentioned below is only required for OpenShift 4.4 and earlier.
To use OpenShift and K10 with CSI-based volume snapshots,
the VolumeSnapshotDataSource feature flag needs to be
enabled. From the OpenShift management console, as an administrator,
select Administration → Cluster Settings → Global
Configuration → Feature Gate → YAML. The resulting
YAML should look like:
apiVersion: config.openshift.io/v1
kind: FeatureGate
metadata:
annotations:
release.openshift.io/create-only: 'true'
name: cluster
spec:
customNoUpgrade:
enabled:
- VolumeSnapshotDataSource
featureSet: CustomNoUpgrade
Accessing Dashboard via Route
As documented here, the K10 dashboard can also be accessed via an OpenShift Route.
Authentication
OpenShift OAuth server
As documented here, the OpenShift OAuth server can be used to authenticate access to K10.
Using OAuth Proxy
As documented here, the OpenShift OAuth proxy can be used for authenticating access to K10.
Kanister Sidecar Injection on OpenShift 3.11
To use the K10 Kanister sidecar injection feature on OpenShift 3.11, make sure that the MutatingAdmissionWebhook setting is enabled. If not, follow the steps below to enable it:
On a control plane node, add the following config to the admissionConfig.pluginConfig section of the /etc/origin/master/master-config.yaml file:
MutatingAdmissionWebhook: configuration: apiVersion: v1 disable: false kind: DefaultAdmissionConfig
Restart control plane services with:
$ master-restart api && master-restart controllers
Validating the Install
To validate that K10 has been installed properly, the following
command can be run in K10's namespace (the install default is
kasten-io) to watch for the status of all K10 pods:
$ kubectl get pods --namespace kasten-io --watch
It may take a couple of minutes for all pods to come up but all pods
should ultimately display the status of Running.
$ kubectl get pods --namespace kasten-io
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kasten-io aggregatedapis-svc-b45d98bb5-w54pr 1/1 Running 0 1m26s
kasten-io auth-svc-8549fc9c59-9c9fb 1/1 Running 0 1m26s
kasten-io catalog-svc-f64666fdf-5t5tv 2/2 Running 0 1m26s
...
In the unlikely scenario that pods that are stuck in any other state, please follow the support documentation to debug further.
Validate Dashboard Access
By default, the K10 dashboard will not be exposed externally.
To establish a connection to it, use the following kubectl command
to forward a local port to the K10 ingress port:
$ kubectl --namespace kasten-io port-forward service/gateway 8080:8000
The K10 dashboard will be available at http://127.0.0.1:8080/k10/#/.
For a complete list of options for accessing the Kasten K10 dashboard through a LoadBalancer, Ingress or OpenShift Route you can use the instructions here.